Soy lecithin
-
Is chocolate with soy lecithin even that bad?
-
I remember discussing this issue with our rodent.
To be conservative, you'd have to find the maximum permitted level for a given food to contain after its addition (varies between countries), but 1% would be a generous value.
50 grams as a food serving with lecithin at 1% yields 0.5 g of lecithin. If this was pure linoleic acid, we would have 500 mg linoleic acid/serving.
The phospholipid research center: current research in phospholipids and their use in drug delivery
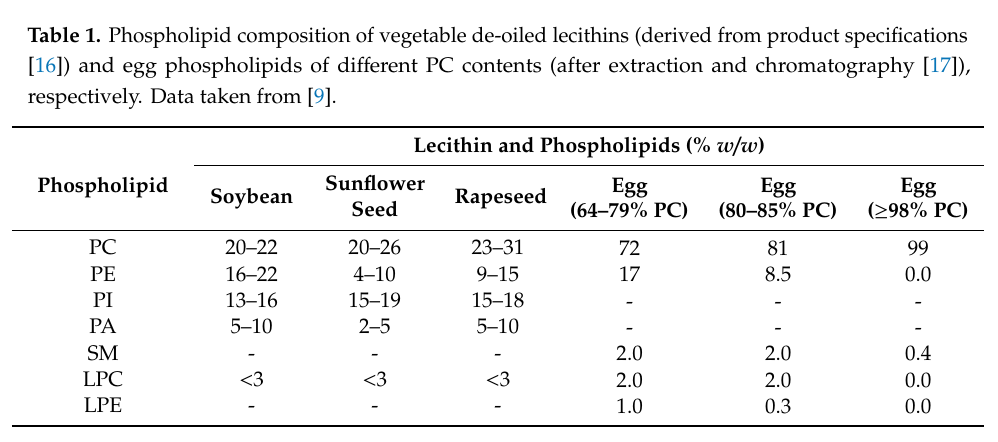
Lecithin is processed and the product may have a higher concentration of phosphatidylcholine.
The use of natural and synthetic phospholipids as pharmaceutical excipients
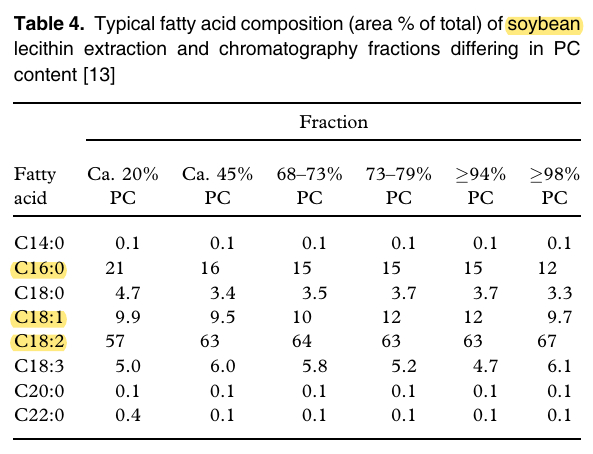
To keep it simple, we can treat other phospholipids of lecithin that may be present as phosphatidylcholine and assume that the only fatty acid occurring is linoleic acid.
Fatty acid (linoleic acid):
- R-COOH
Fatty acyl (linoleoyl):
- R-CO-
- Dilinoleoyl-phosphatidylcholine – glycerophosphocholine
(whole molecule minus the non-fatty fraction)
⠀ - 782 g/mol – 257 g/mol = 525 g/mol (corresponding to the 2 'linoleoyls')
⠀ - 782 g/mol → 100%
- 525 g/mol → ~70%
500 mg PC/serving × 70% = ~350 mg LA/serving
The values above were inflated. As an example of how low it can be, I contacted a large company to ask how much soy lecithin they add to their whey protein, and they replied that it contains 0.1 g lecithin/kg whey protein (0.01%).
Lecithin per serving:
- 15 g × 0.01 = 0.0015 g = 1.5 mg lecithin/serving
Discounting the non-fatty fraction:
- 1.5 mg × 70% → ~1 mg fatty acids/serving
Discounting the other fatty acids:
- 1 mg × 70% → ~0.7 mg linoleic acid/serving (~0.0007 g/serving)
Nutrient Ranking Tool | MyFoodData
Phospholipids are remodeled during digestion.
Potential Roles of Fatty Acids and Lipids in Postharvest Needle Abscission Physiology
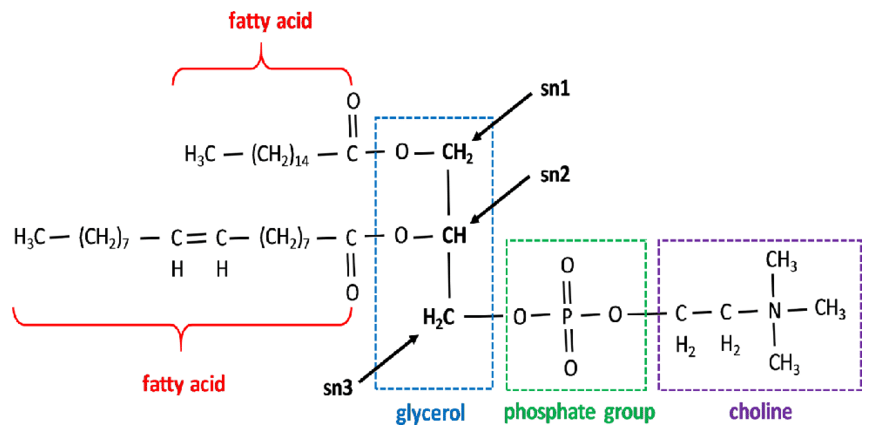
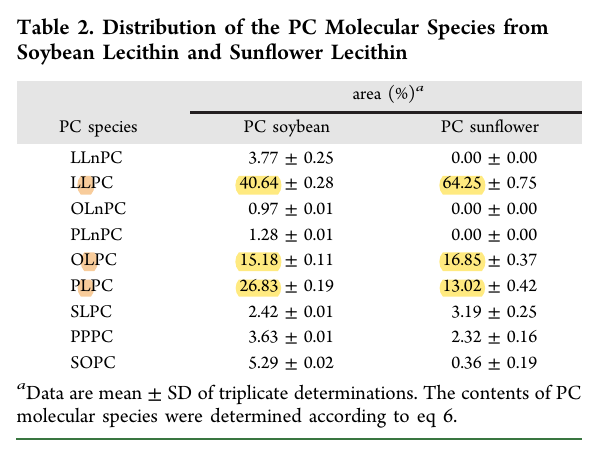
The abbreviation is in order (sns: 1, 2, 3). Example: LLPC is Linoleoyl, Linoleoyl and Phosphorylcholine.
The sn-2 position is known as the susceptible to remodeling during digestion (after the action of phospholipase A2). In contrast, the sn-1 position might remain intact.
It would be preferable for linoleoyl not to occur at the sn-1 position because of this, but at least linoleoyl in the middle (sn-2) is a common pattern in these phospholipids and can be substituted for other fatty acyls. The released fatty acid can be absorbed in free form, but not incorporated in the phospholipid.