Enhanced Selenium Supplement Extends Lifespan
-
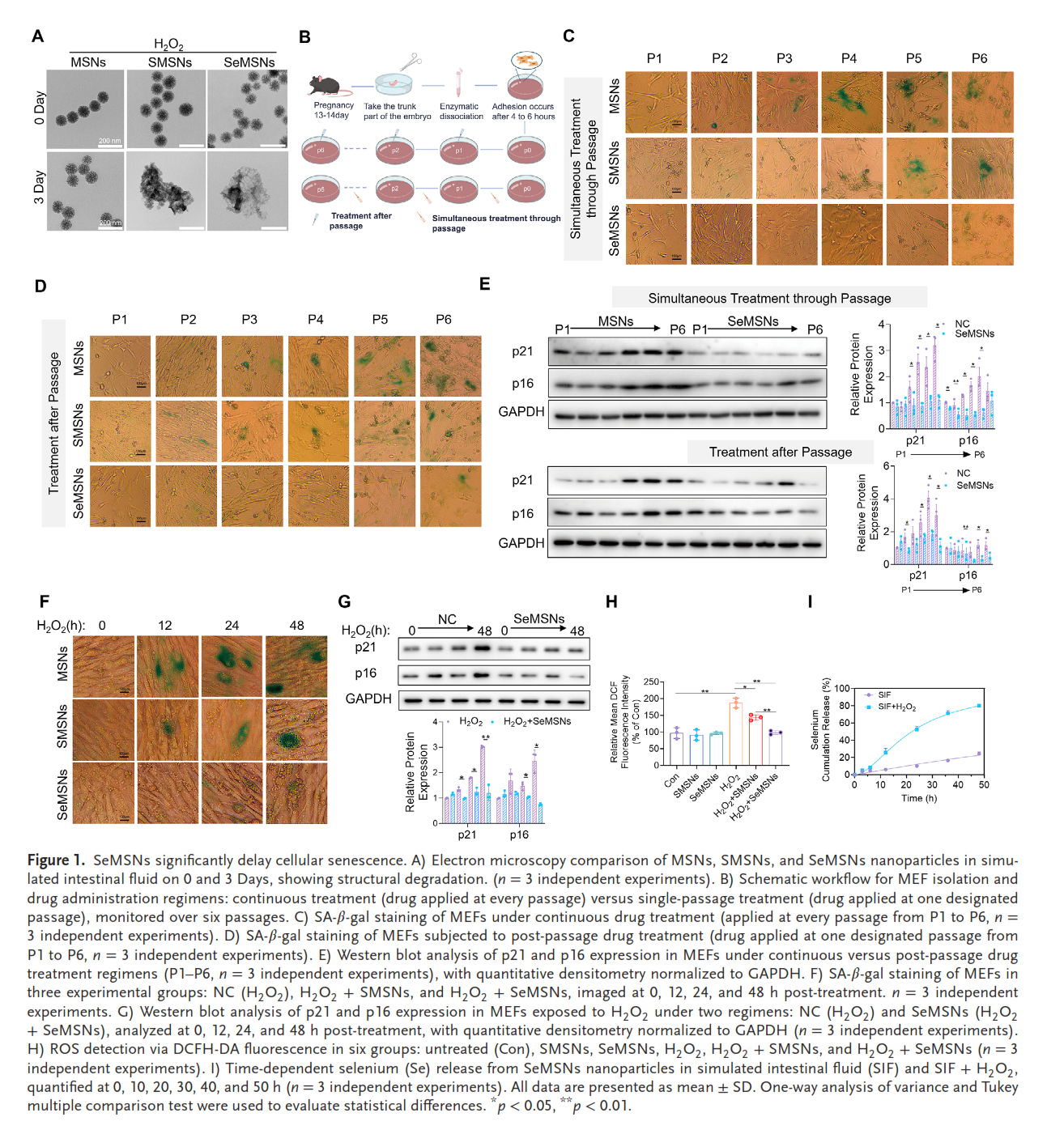
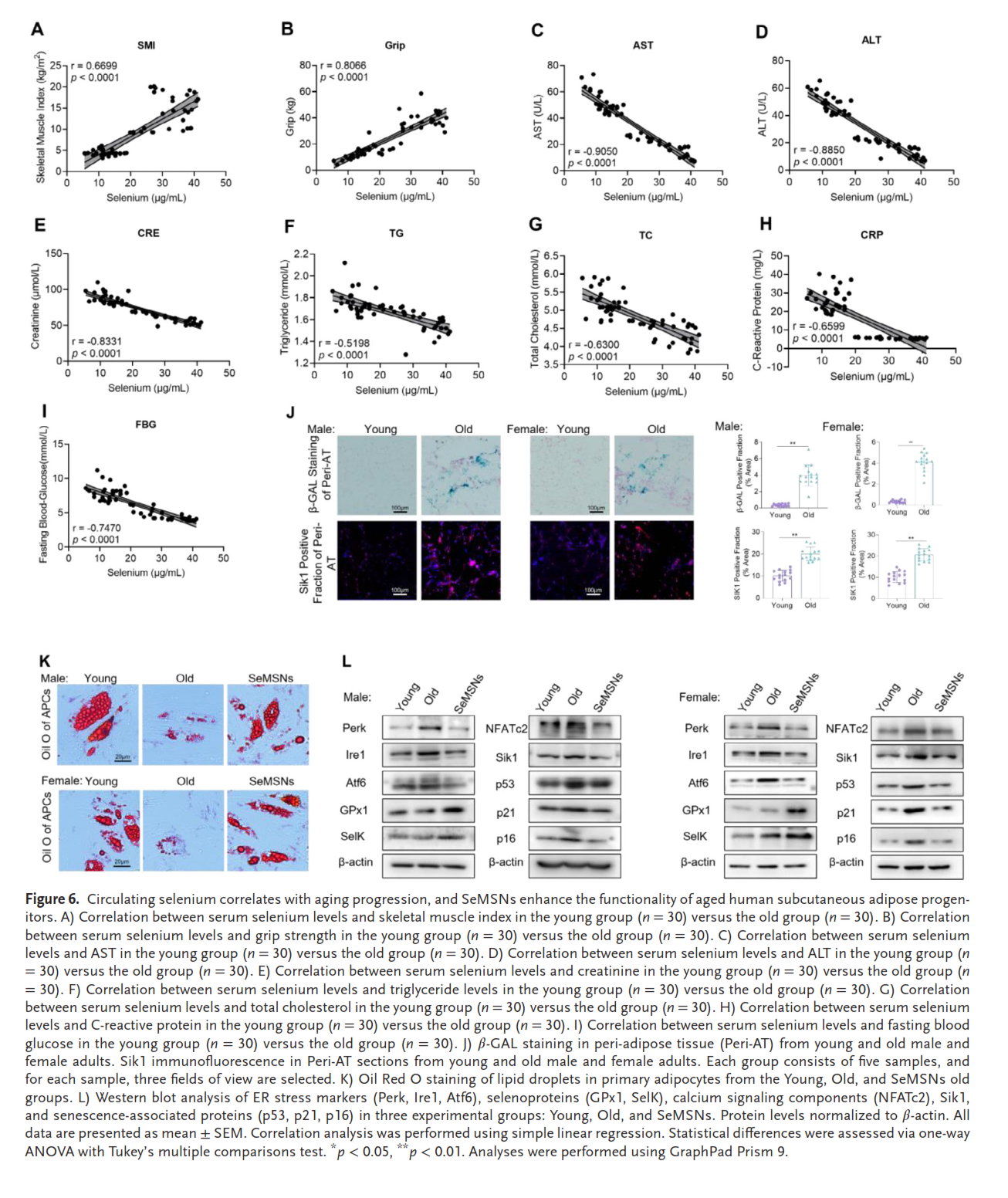
Selenium supplementation has potential in treating aging-related disorders like neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases, but its use is limited by poor bioavailability, a narrow therapeutic window, and unclear mechanisms. To overcome this, redox-dual-responsive diselenide-bridged mesoporous silica nanoparticles (SeMSNs) are developed. SeMSNs effectively reduce oxidative stress and downregulate senescence markers (p16, p21), suppressing senescence in both naturally aged primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and H2O2-induced HEK-293T cells. They show prolonged antioxidant effects (p < 0.05) and lower cytotoxicity (p < 0.01) than commercial selenomethionine. In aged mice, SeMSNs extend lifespan, reduce frailty, and improve age-related conditions, including muscle atrophy, renal dysfunction, cognitive decline, and hepatic steatosis, while restoring metabolic balance. They outperform conventional organically-bridged mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) and disulfide-bridged MSNs (SMSNs) (p < 0.01). Mechanistically, SeMSNs upregulate selenoproteins (GPx1, SelK), suppress endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated calcium release, maintain calcium homeostasis, and inhibit NFATc2-driven Sik1 transcription, reducing p21/p16. Clinical data confirm an inverse correlation between selenium levels and aging biomarkers (p < 0.0001). SeMSNs also restore adipogenic differentiation in human adipose progenitor cells via calcium-NFATc2-Sik1 signaling. These results demonstrate the superiority of SeMSNs over traditional selenium forms, providing a nanotherapeutic strategy to combat multi-organ aging and promote healthy longevity.