Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) : Dichotomous Impact
-
From:
Inducible nitric oxide synthase: what difference does it make?"The [iNOS} dichotomy is sometimes manifest at different times or sites in the same experimental setting."
"In both infection and inflammation, iNOS appears to act both as a direct effector and as a regulator of other effectors."
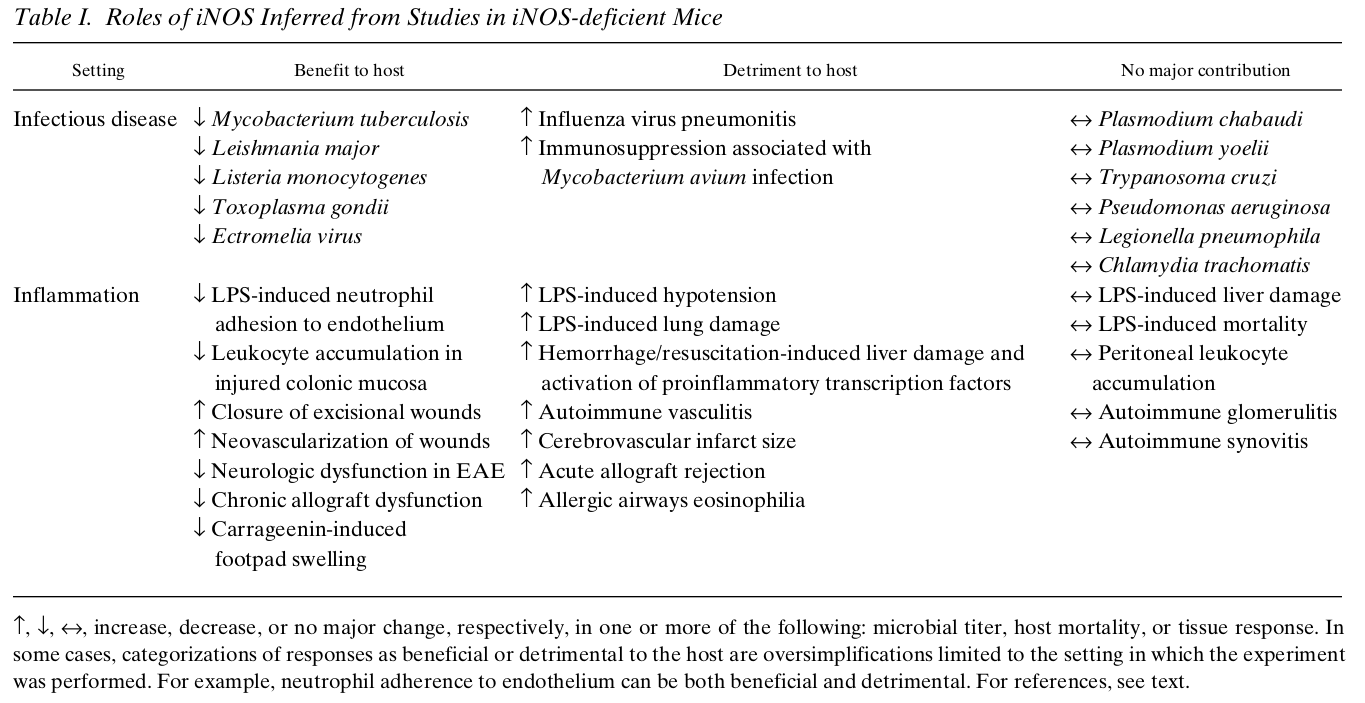
"..the cytotoxic and proinflammatory potential of iNOS advances the case for its therapeutic inhibition in those of the diseases discussed above that are not thought to be infectious in etiology, such as Alzheimer’s disease, hemorrhagic shock/resuscitation, late-phase vasoocclusive stroke, inflammatory bowel disease, and rheumatoid and osteoarthritis, or in those infectious diseases where the inflammatory effect of iNOS appears to outweigh its antimicrobial effect, such as influenza pneumonia. However, the antiinflammatory role of iNOS emphasizes the possibility of adverse consequences attendant on its inhibition."
-
Ethanol extract of propolis (EEP) inhibits nitric oxide synthase gene expression and enzyme activity
I long hoped there would be anything else but MBlue + Red Light to inhibit NO. And voilà: it's the caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), which is "identified as a major peak in the chromatogram of EEP".
From the abstract:
"EEP inhibited the iNOS promoter activity induced by LPS plus IFN-g through the NF-kB sites of the iNOS promoter. In addition, EEP directly interfered with the catalytic activity of murine recombinant iNOS enzyme. These results suggest that EEP may exert its anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the iNOS gene expression via action on the NF-kB sites in the iNOS promoter AND by directly inhibiting the catalytic activity of iNOS."
[emphasis mine.]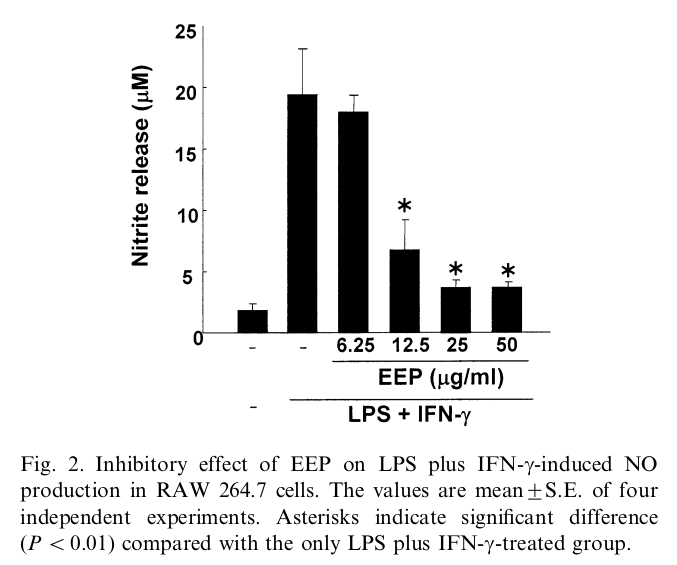
Preparation of extract from the paper:
Coarsely powdered propolis (100 g) was extracted with 10 volumes of 95% ethanol for 2 weeks. The ethanol extract was filtered, evaporated, and lyophilized to give the dry ethanol extract (33.3 g).
In Anti-inflammatory Effect of Propolis through Inhibition of Nitric Oxide Production on Carrageenin-Induced Mouse Paw Edema, even smaller amounts of extract were successfully used:
Because lyophilized ethanol extract of propolis used in the present study is equivalent to 18.5 mg propolis per 100 ml, 16) 1: 1000 and 1: 100 dilutions of propolis correspond to 1.85 and 18.5 mg/kg, respectively. Therefore, the propolis used in the present study was 5.4—54 times more potent than that reported by Borrelli et al. ... though there was a difference between mouse and rat.
-
@Lejeboca - Thanks for the links. iNOS may have a dichotomous impact but it appears to be mostly negative.
Peatbot.com: iNOS, or inducible nitric oxide synthase, is an enzyme that produces nitric oxide (NO) in response to certain stimuli, such as inflammatory signals. It is one of the three isoforms of nitric oxide synthase, the others being endothelial (eNOS) and neuronal (nNOS). iNOS is not typically expressed under normal conditions but is induced in response to inflammatory cytokines and other stress signals.
The ethanol extract of propolis (EEP) article (2002) is interesting and it is a great find. The much later article Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase: Regulation, Structure, and Inhibition (2020)
Abstract
A considerable number of human diseases have an inflammatory component, and a key mediator of immune activation and inflammation is inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), which produces nitric oxide (NO) from L-arginine. Overexpressed or dysregulated iNOS has been implicated in numerous pathologies including sepsis, cancer, neurodegeneration, and various types of pain. Extensive knowledge has been accumulated about the roles iNOS plays in different tissues and organs. Additionally, X-ray crystal and cryo-EM structures have shed new insights on the structure and regulation of this enzyme. Many potent iNOS inhibitors with high selectivity over related NOS isoforms, neuronal NOS (nNOS) and endothelial NOS (eNOS), have been discovered, and these drugs have shown promise in animal models of endotoxemia, inflammatory and neuropathic pain, arthritis, and other disorders. A major issue in iNOS inhibitor development is that promising results in animal studies have not translated to humans; there are no iNOS inhibitors approved for human use. In addition to assay limitations, both the dual modalities of iNOS and NO in disease states (i.e., protective vs. harmful effects) and the different roles and localizations of NOS isoforms, create challenges for therapeutic intervention. This review summarizes the structure, function, and regulation of iNOS, with focus on the development of iNOS inhibitors (historical and recent). A better understanding of iNOS’ complex functions is necessary before specific drug candidates can be identified for classical indications such as sepsis, heart failure, and pain; however, newer promising indications for iNOS inhibition, such as depression, neurodegenerative disorders, and epilepsy, have been discovered.
-
@DavidPS , the main takeaway from the paper in the OP is that sometimes you absolutely want to suppress NO (and iNOS) and sometimes you might not want to do so. The former is broadly true for autoimmune conditions and the latter is for true infections, esp. those with which the body has to deal with whatever means it can.
Thanks for the article Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase: Regulation, Structure, and Inhibition (2020) !
It will take me some time to digest its 45 pages . The abstract, however, already points to the dichotomy, "both the dual modalities of iNOS and NO in disease states (i.e., protective vs. harmful effects)" indeed.
. The abstract, however, already points to the dichotomy, "both the dual modalities of iNOS and NO in disease states (i.e., protective vs. harmful effects)" indeed. -
@Lejeboca - thank you for taking the time to respond. I got things twisted around in my mind and it is embarrassing.
I think of the relationship between the eNOS and iNOS isoforms of nitric oxide synthase as being analogous to Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde. The "i" in iNOS is related to inflammation, ischemia and intoxication all of which are generally bad. Whereas the "e" is related to the endothelium and is very healthy to have on board. Caldwell Esselstyn had his cardiac patients eat greens all day to maintain high levels of eNOS as part of his successful plan to reverse heart disease.
In 1998, the Noble Prize in Medicine was awarded to 3 people for their work on NO (see press release). This encouraged people to supplement with L-arginine to lower their blood pressure. The excessive iNOS from the supplementation had long term consequences that were not good.
Incidentally, aspirin releases eNOS.
Aspirin induces nitric oxide release from vascular endothelium: a novel mechanism of action (2009)