L-proline supplementation is very protective in K pneumoniae pneumonia (common in hospitals, resistant to antibiotics)
-
- The bacterium typically colonizes human mucosal surfaces of the oropharynx and gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Once the bacterium enters the body, it can display high degrees of virulence and antibiotic resistance. Today, K. pneumoniae pneumonia is considered the most common cause of hospital-acquired pneumonia in the United States, and the organism accounts for 3% to 8% of all nosocomial bacterial infections
feeding ~ +3g x2 human equivalent proline a day
L-proline
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334253009_L-Proline_protects_mice_challenged_by_Klebsiella_pneumoniae_bacteremia @DavidPS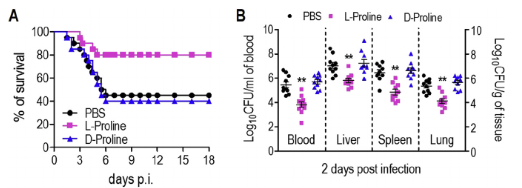
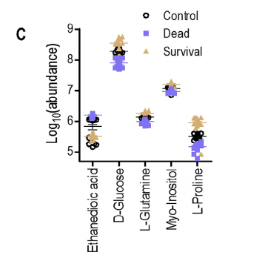
80% survival using proline instead of 40% , reduces bacterial countanimals who died had lower proline & glucose
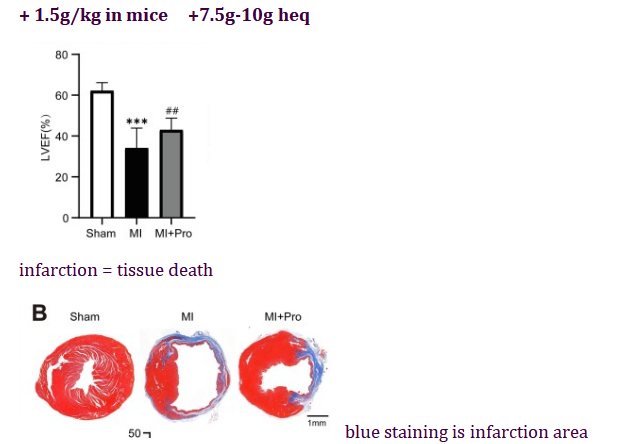
it's also helpful for heart regeneration after a heart attack
(proline main amino acid for stem cell proliferation)
used after induction
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006295220302999#s0085
-
Thanks for the heads up on these articles. I immediately went to chronometer.com to confirm that I am getting enough proline in my diet. I have been tracking my diet for several weeks and I am getting 4-7 grams of proline daily. So I am safe to visit friends who are in hospitals.
-
The Multifaceted Roles of Proline in Cell Behavior
Herein, we review the multifaceted roles of proline in cell biology. This peculiar cyclic imino acid is: (i) A main precursor of extracellular collagens (the most abundant human proteins), antimicrobial peptides (involved in innate immunity), salivary proteins (astringency, teeth health) and cornifins (skin permeability); (ii) an energy source for pathogenic bacteria, protozoan parasites, and metastatic cancer cells, which engage in extracellular-protein degradation to invade their host; (iii) an antistress molecule (an osmolyte and chemical chaperone) helpful against various potential harms (UV radiation, drought/salinity, heavy metals, reactive oxygen species); (iv) a neural metabotoxin associated with schizophrenia; (v) a modulator of cell signaling pathways such as the amino acid stress response and extracellular signal-related kinase pathway; (vi) an epigenetic modifier able to promote DNA and histone hypermethylation; (vii) an inducer of proliferation of stem and tumor cells; and (viii) a modulator of cell morphology and migration/invasiveness. We highlight how proline metabolism impacts beneficial tissue regeneration, but also contributes to the progression of devastating pathologies such as fibrosis and metastatic cancer.