PQQ Pyrroloquinoline quinone (found in space dust) - dietary intake
-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8169668/
In the first experiment, weanling female BALB/c mice were adapted to a chemically-defined diet containing 0, 100, 200, 300, 1000, or 5000 ng PQQ/g of diet. The mice were bred and their reproductive performance and surviving offspring were assessed for 20-wk.
Reproductive outcome was markedly compromised for the groups most deprived of PQQ. Supplemented groups (> or = 1000 ng PQQ/g diet) had 8 pups/litter compared with 4-5 pups/litter in the PQQ-deprived groups (< or = 300 ng PQQ/g diet).
Of the pups surviving to weaning, 8 of 10 survived when PQQ was added to the diet (> or = 300 ng PQQ/g diet) compared with 4 of 10 in the PQQ/deficient group. The apparent requirement for PQQ for optimal growth of surviving neonates was estimated to be > 300 ng PQQ/g of diet.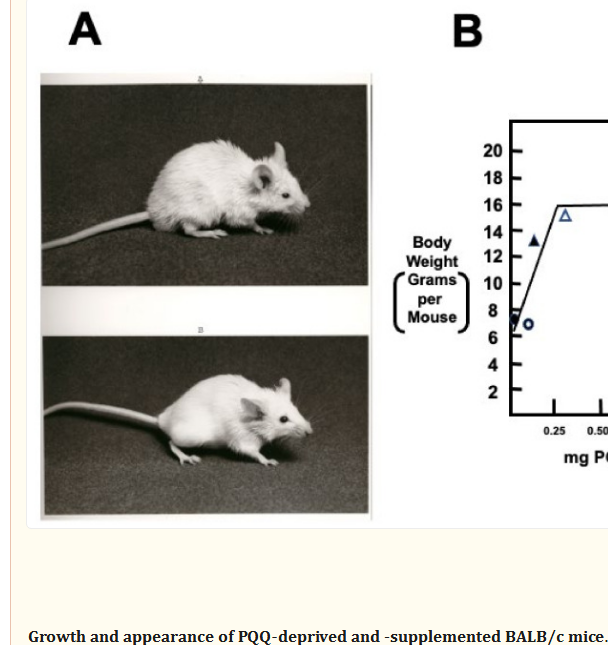
- Quinone cofactors may have had a role in early aerobic life on Earth. PQQ dependent methanol dehydrogenase has been found in many different types of bacteria including one archaea21. Recent results from the CIDA (Cometary and Interstellar Dust Analyzer) instrument on the Stardust spacecraft found numerous quinones, including ortho-quinones, in interstellar dust mainly from comet p/ Wild222.
pyridyl- and quinoline- quinones were the most likely compounds with the largest peak in the positive ion spectrum at m/z 331 which corresponds to PQQ23.
This has given rise to speculation that PQQ from interstellar dust played a key catalytic role in the early Earth. It is interesting to note that PQQ is known to only be made bacterially on Earth and that all the evidence strongly indicates that it is peptide derived.
As far as we know, there are no bacteria or proteins in space to form the PQQ found in interstellar dust. This raises many interesting questions about the presence of PQQ and the origin of its biosynthesis.
Identification of lactate dehydrogenase as a mammalian pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ)-binding protein
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4882622/#sec8
(lowers lactate, increases nad+) PQQ bound to LDH enhances NADH oxidation to NAD+ and pyruvate productionprotective effect works in very low nM concentration for some things (1mg intake daily should be good) https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9158787/
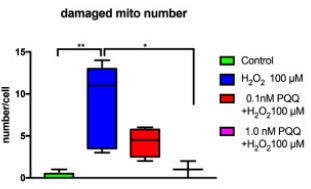
mitochondria number changes
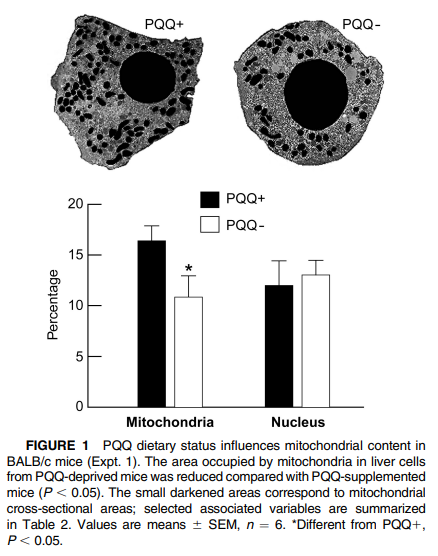
https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/136.2.390In the diet it reacts quick with things so isnt found much as free form, u largely get derivatives https://michaelrucker.com/functional-supplements/pqq-disodium-salt/ e.g Imidazolopyrroloquinoline (IPQ)
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6994848/#sec3 similar effects
so cant see if you're hitting the requirement (500ug) as pqq form in foods https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1136652/?page=2Its seen as a vitamin like compound. some enzymes might rely on it, or at least are boosted by it
acute effect as disodium salt form orally in drinking water, 20mg/kg mice didnt raise ATP. 20mg/kg injected i,p did https://actaneurocomms.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40478-023-01642-6#Sec16
but i.p in rats caused kidney toxicity https://europepmc.org/article/med/2546903Some liver and kidney toxicity mentioned ~20mg/kg rats, or >15mg/kg given i.p, but not at single digit, so probably best to keep this on the low mg end
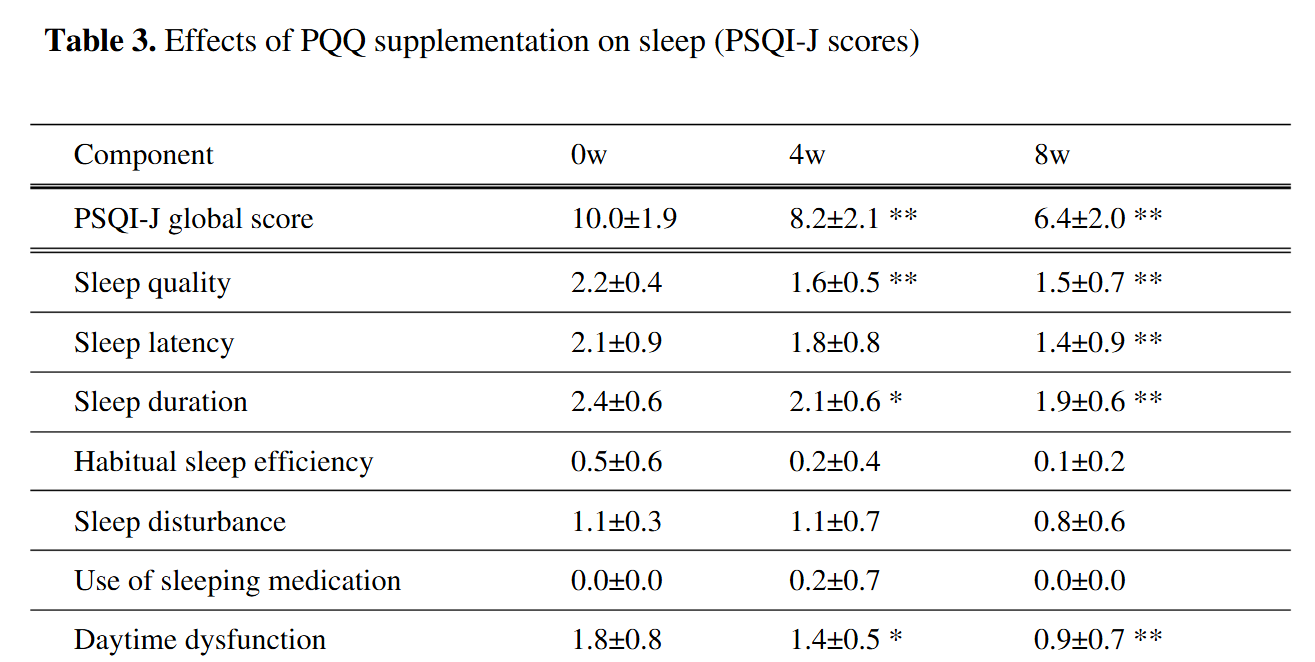
- High-dose PQQ (20 mg/kg) produced renal and hepatic toxicity, PQQ (3 mg/kg) given at the onset of reperfusion was the lowest dose that had no evident renal or hepatic toxicity and significantly reduced infarct sizesleep improved well (scale 0 - 3 with 3 being highest dysfunction for individual scores) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281323256_Effects_of_Oral_Supplementation_with_Pyrroloquinoline_Quinone_on_Stress_Fatigue_and_Sleep by 8 weeks
- Quinone cofactors may have had a role in early aerobic life on Earth. PQQ dependent methanol dehydrogenase has been found in many different types of bacteria including one archaea21. Recent results from the CIDA (Cometary and Interstellar Dust Analyzer) instrument on the Stardust spacecraft found numerous quinones, including ortho-quinones, in interstellar dust mainly from comet p/ Wild222.
-
@cs3000 great writeup, I'll simply add the summary table from this article
Table 1.
Pyrroloquinoline Quinone: Novel Attributes.
Attribute Description PQQ is required for essential physiological functions PQQ is one of only a few nutritionally important biofactors for which a nutritional deficiency can be defined in multiple species of eukaryotes [9,60,61,66,83]. PQQ has been tentatively identified as a component of interstellar dust [83]. Thus, PQQ may have been present throughout early biological conception and evolution. PQQ is also a plant growth factor [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51], i.e., for animals and humans, there has been constant exposure to PQQ [83]. The apparent need for PQQ is nutritionally attainable without the need for supplementation PQQ effects are elicited in the nM to μM range of exposure, in contrast to the mM concentrations needed for other biofactors [9,60,61]. PQQ and its derivatives, such as imidazopyrroloquinoline (IPQ) compounds, are found in the milk of mammals in concentrations like vitamins, such as folate, riboflavin and, biotin [12,75]. In rodents, PQQ appears essential for reproduction [60,61,136]. PQQ aids in sustaining cellular NAD+ levels and mitochondriogenesis PQQ acts as an accessory factor for lactate and potentially other dehydrogenases in NADH oxidation to NAD+ [18,19]. Accordingly, the effects of PQQ exposure mimic those of cellular NAD+ (e.g., sustaining mitochondriogenesis [11,165]. PQQ stimulates sirtuin activity Sirtuins modulate the activity of factors involved in DNA repair and mitochondriogenesis [23]. PQQ stimulates the expression of proteins in the sirtuin family of enzymes and, by sustaining NAD+ levels, optimizes NAD+, a sirtuin cofactor and co-substrate [11,165]. Relationships involving PQQ are important to the aging process, immunity, and ROS defense PQQ exposure increases longevity in models used in the study of aging [53], improves immune responsiveness to cytokines [9,70,145], and acts as a potent redox cycling agent that helps maximize ROS defense [9,12,13,16,107,145]. PQQ is associated with the attenuation of clinically relevant dysfunctions such as ischemia, neurogenic losses, inflammation, and lipotoxicity. PQQ is neuroprotective and appears to improve memory [74,155,162,163,164]. PQQ protects NMDA mediated receptors in neurological injury. PQQ can reverse hepatic steatosis and has potential as a therapeutic for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) [107,145]. PQQ also influences serum lipid metabolism in ways relevant to protection from heart disease [147]. Moreover, in models of ischemia and reperfusion injury, the cardioprotective effectiveness of PQQ is equivalent to β1-selective adrenoceptor antagonists, such as metoprolol [149]. PQQ alleviates jejunal mucosal inflammatory injury in animal models by inhibiting events associated with NF-κB-related pathways and improving the imbalance of colonic microbiota caused by various agents [9,107,145]. As noted by Naveed et al. [49], inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract has a strong association with ROS genesis. PQQ, as a ROS scavenger, acts as a protectant. PQQ also acts to reduce C-reactive protein and IL-6 levels [61]. PQQ is safe. The no observed effect level (NOAEL) for PQQ has been determined to be 400 mg/kg bw/day in a sub chronic toxicity study in rats. By applying a safety margin of 100, it can be concluded that doses up to 4 mg/kg BW/day or 240 mg/person/day would be safe in adult humans weighing 60 kg [87,88,89,90]. -
@stag
 good one , even 1 mg daily should be good for our intestine
good one , even 1 mg daily should be good for our intestinea little of this goes a long way just 0.8mg/kg diet Pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium in pigs (most similar intestine to humans vs rodents)
https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo02609f
Lowered inflammation, decreased mortality / diarrhea and increased nad+ in cytosol
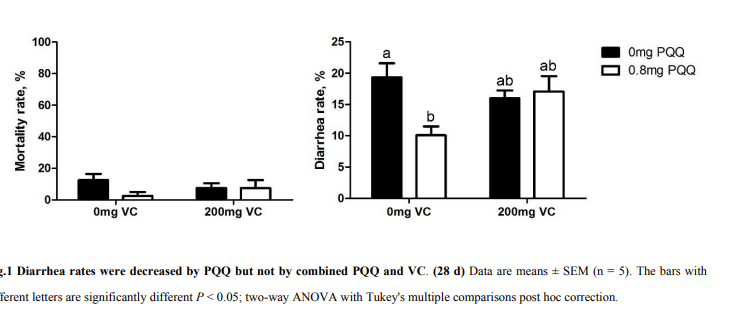
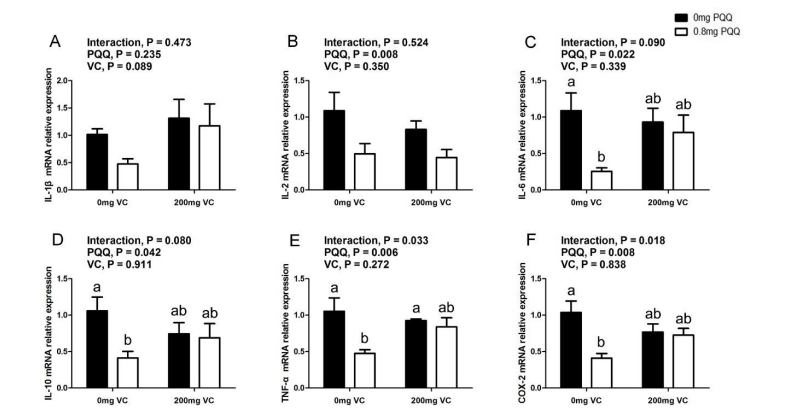
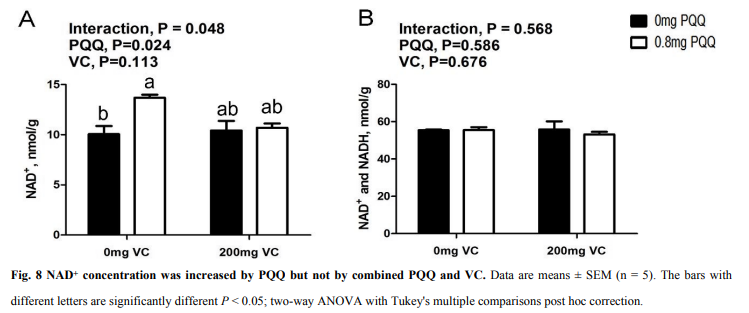
key to take separately from antioxidants like vit C otherwise effect lost
effect might seem odd being oxidized form (e,g like ROS an ability to remove electrons), when the PQQ form (small amount) interacts with NADPH or glutathione it forms a potent free radical remover + vit E recycler (after vitamin E reacts with PUFA forming α-tocopheroxyl radical) that gets re-used many times over
PQQ can react with NAD(P)H or thiol compounds such as glutathione to form pyrroloquinoline quinol (PQQH2) to exert its antioxidant function.16, 17 PQQH2 is a form of PQQ in tissues with strong oxygen free radical scavenging ability, far stronger than that of VC and vitamin E.
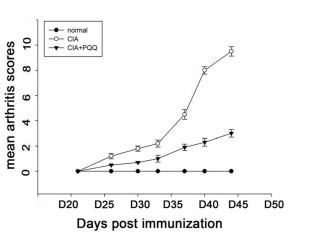
arthritis progression https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0245-7
e coli 3mg per kg diet villus height in jejunum
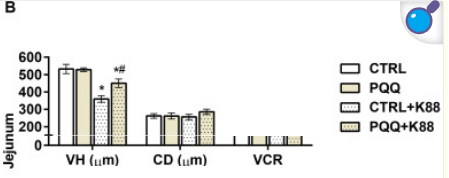
-
@cs3000 this one is interesting too: Pyrroloquinoline quinone prevents developmental programming of microbial dysbiosis and macrophage polarization to attenuate liver fibrosis in offspring of obese mice
We further demonstrated that bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were polarized toward an inflammatory state at 8 weeks of age and that a potent antioxidant, pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ), reversed BMDM metabolic reprogramming from glycolytic toward oxidative metabolism by restoring trichloroacetic acid cycle function at isocitrate dehydrogenase.