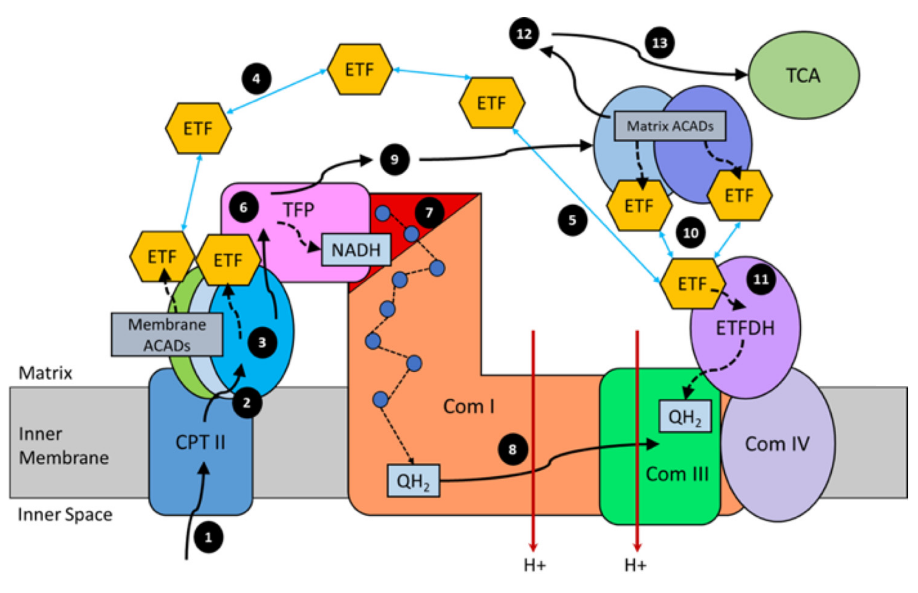
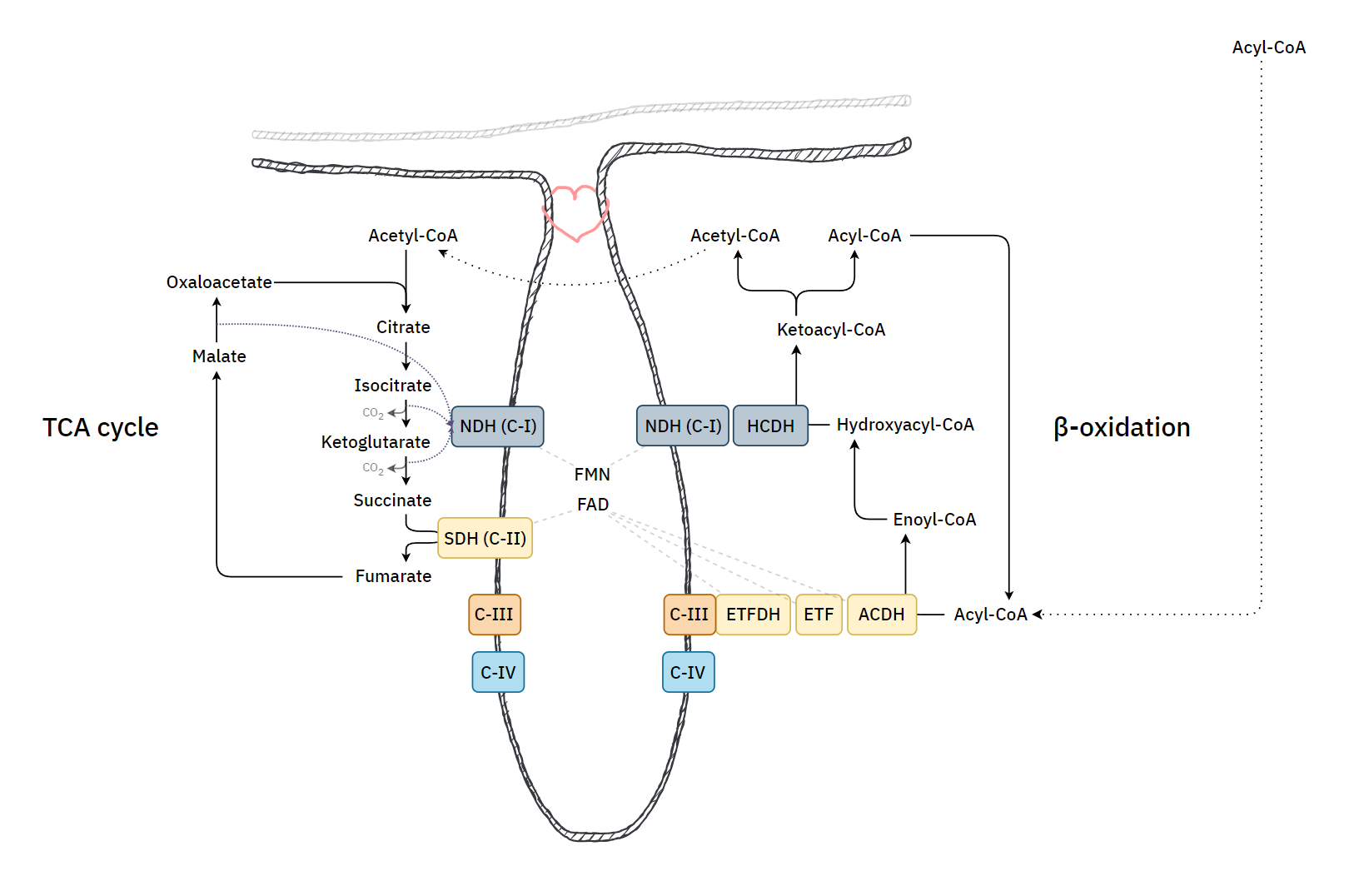
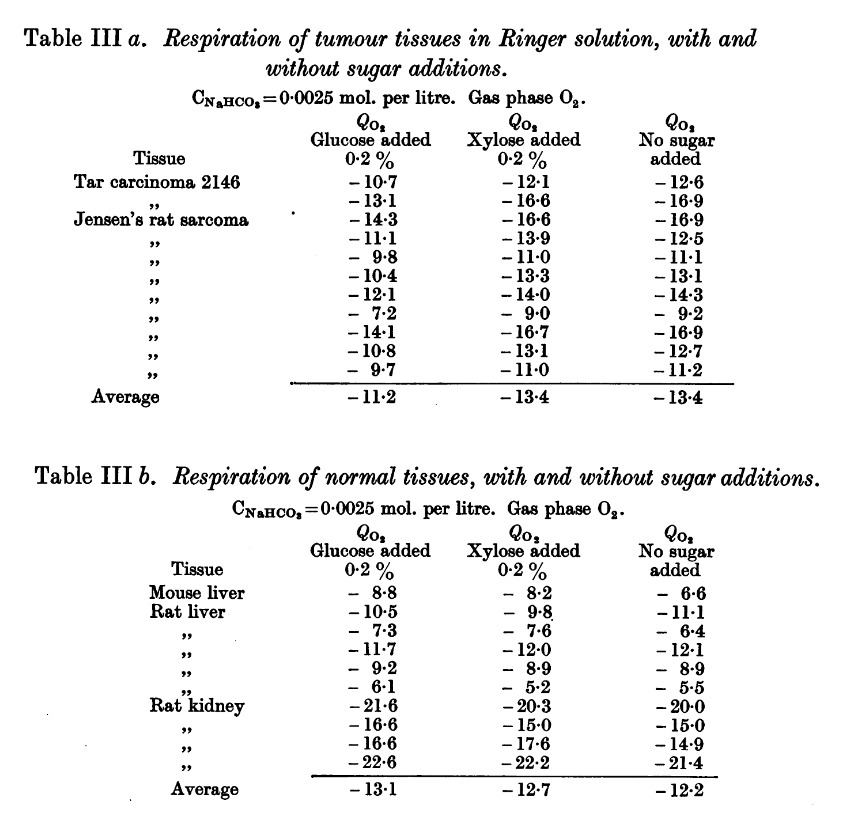
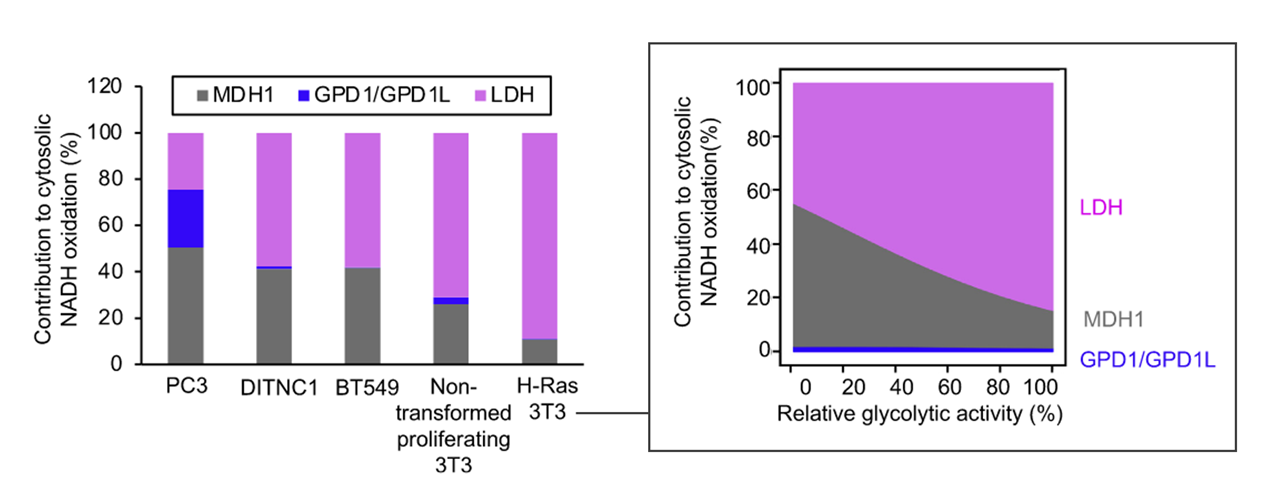
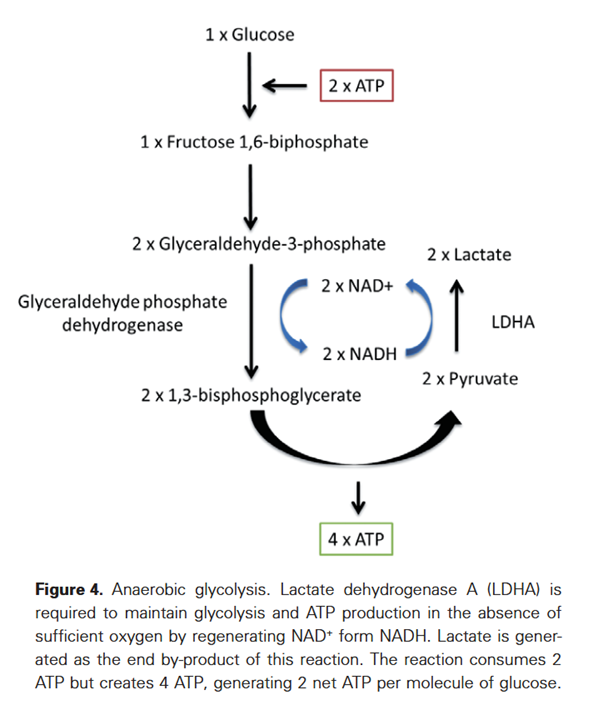
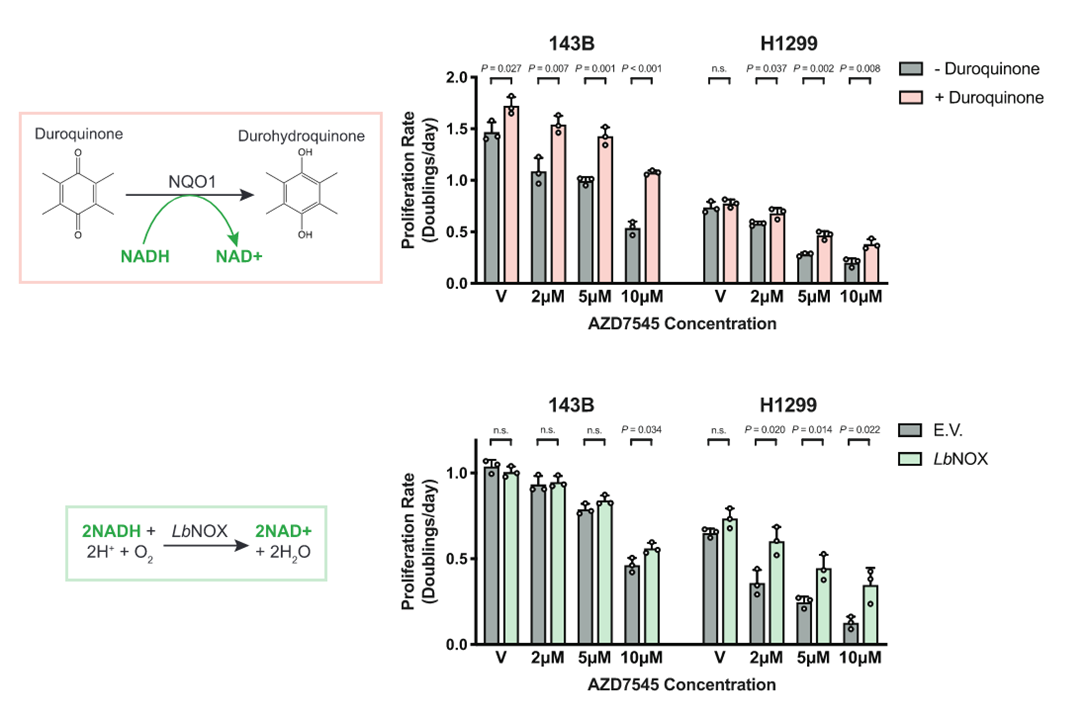
Why not make an impartial compilation of experiments on cancer and group them according to the effect of extra glucose (without additional factors) on cancer cells: supporting versus hindering proliferation? We can't go by the majority, but it's a starting place to question.
The line of thought would not be far from the idea that more glutamine should be delivered to cancer cells because they overconsume it to the point of depletion. Deficiencies can promote a more aggressive behavior, but it's not that we need the encouragement to load up on glutamine to compensate.
A condition of generalized scarcity is common, and this would call for the replenishment of many compounds. For example, immune cells can also compete with cancer cells for glucose, but also glutamine and other nutrients that may be rapidly used up.
Gerson's approach consisted of a moderate caloric intake, better distributed in smaller and more frequent meals, which leans in favor of a controlled exposure. If I was against dietary toxins, I wouldn't mention him often because the original therapy asked for minimal fats. Sometimes tumors have a person attached to them, and the person must be fed on occasion. Looking for potential downsides helps to identify and counteract them, but also avoids cults*. In case anyone knows superior dietary therapies to that of Gerson, I wouldn't mind relegating it, no matter how unconventional.
- *Reflected on a thread such as our "Can glucose loading cure everything?"
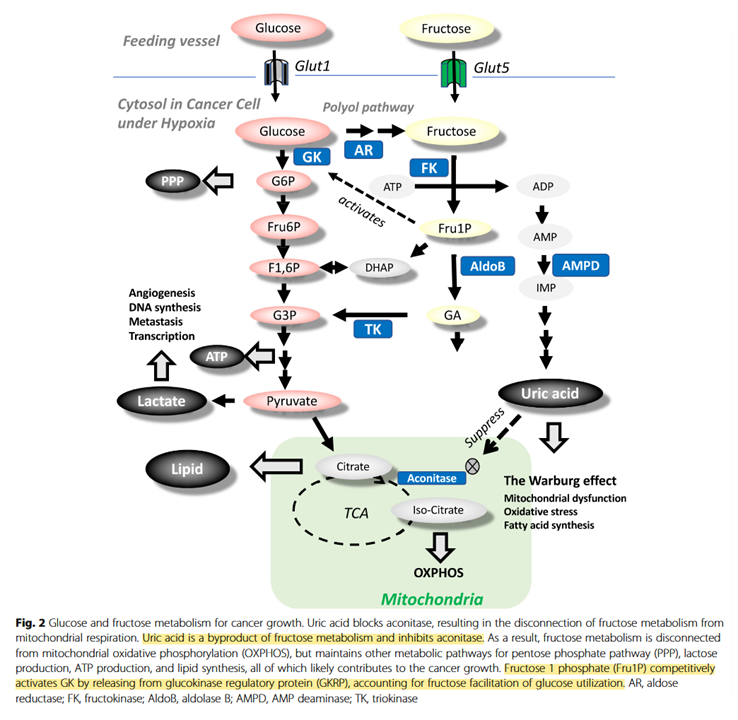
It would be good to know how relevant fructose-1-phosphate would be on tissues that don't express ketohexokinase or glucokinase (a variant of hexokinase). Also, how high uric acid levels have to be to affect aconitase.
But it makes more sense to seek local nutrient repletion when you can target the misbehavior or exploit it.
In the previous experiment, they first manipulated Hypoxia-inducible Factor (HIF) to lift some of the metabolic inhibitions and only then pound glucose with insulin, intending to provoke oxidative stress. Otherwise, the effect was insignificant.
It's not difficult to picture glucose lessening the oxidative burst from vitamin C therapy when not much else is done to manipulate the fermentation pattern.
NADPH homeostasis in cancer: functions, mechanisms and therapeutic implications
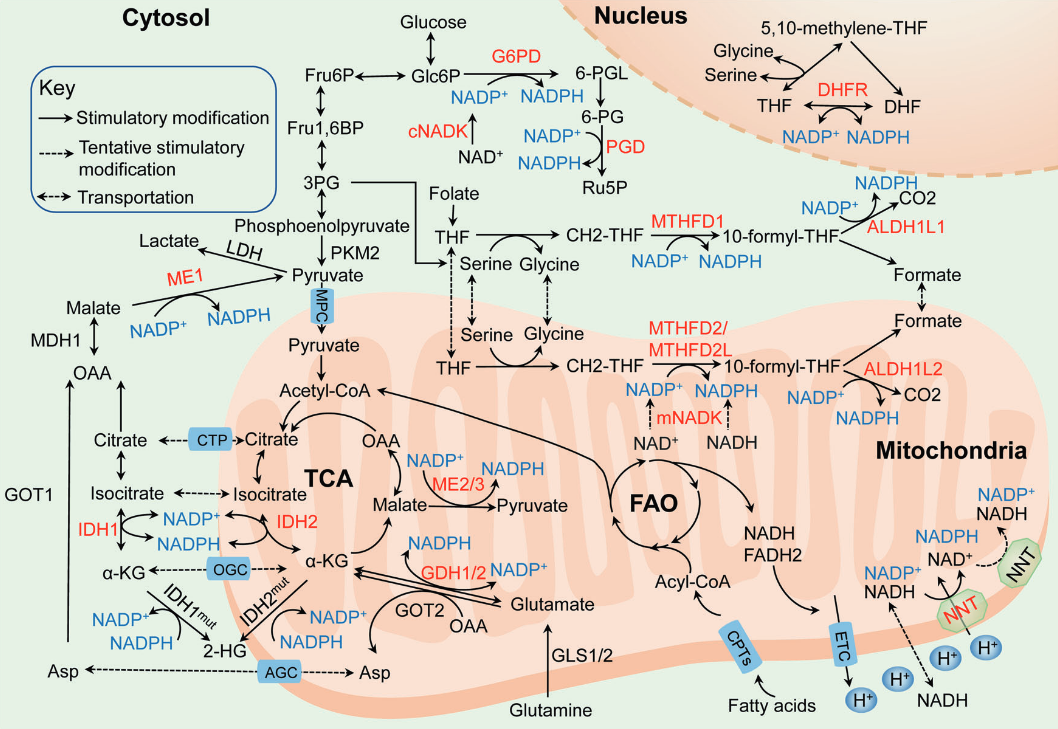
| NADPH-producing enzyme |
Origin of main substrate |
| G6PDH |
Glucose |
| PGDH |
Glucose |
| ME |
Glutamine, glucose |
| IDH |
Glutamine |
| MTHFDH |
Glucose |
| ALDH |
Glucose |
| GDH |
Glutamine |
| NNT |
Glutamine, fatty acids, glucose |
Glucose may also spare glutamine in antioxidation.
By the great Matthew Vander Heiden and Sophia Lunt:
Aerobic Glycolysis: Meeting the Metabolic Requirements of Cell Proliferation
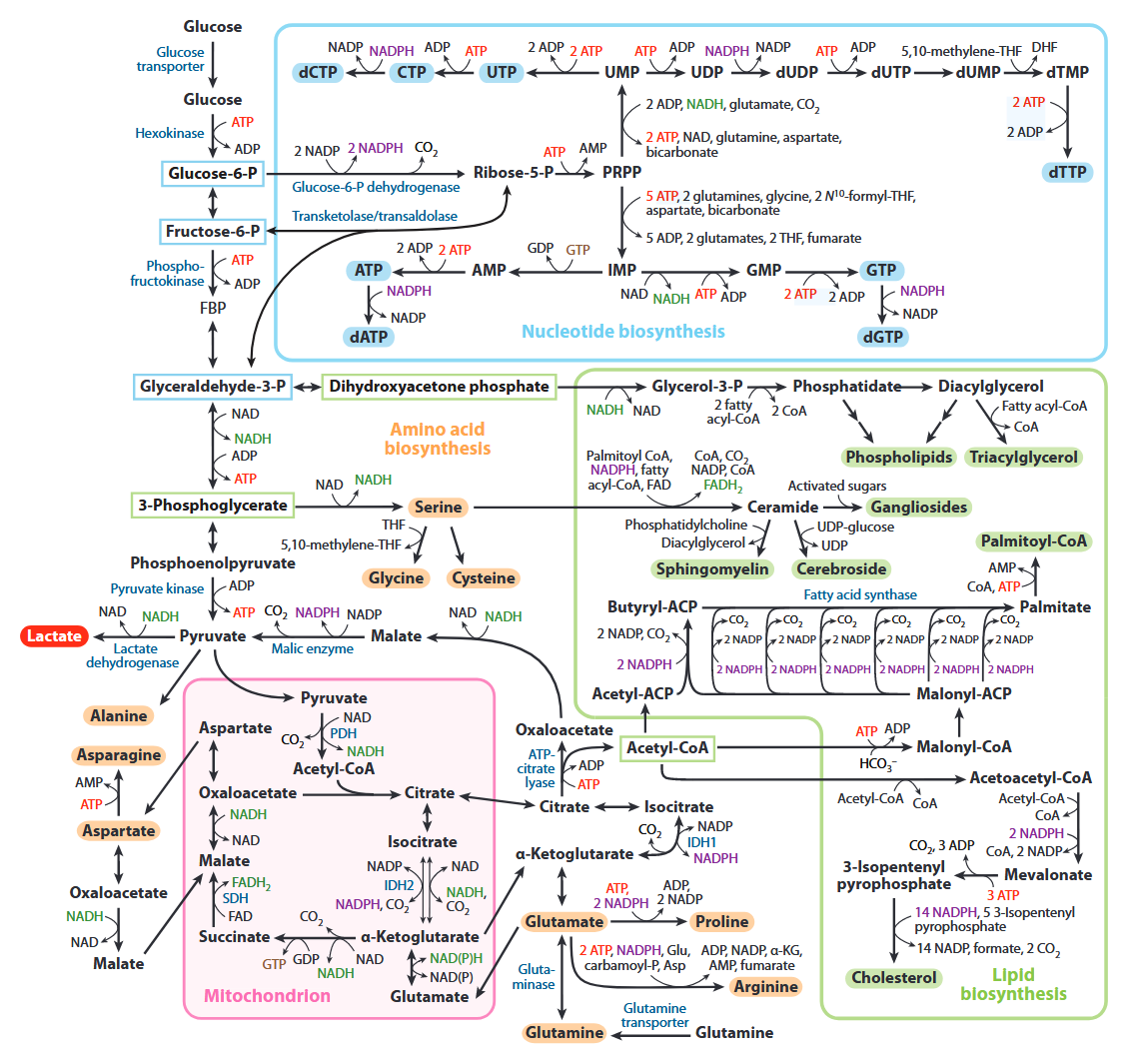
All of the carbons that occur in nucleotides can conceivably come from glucose. It's absurd.
| Carbon source |
Derivation |
Carbons donated |
| Ribose |
Glucose →→ ribose |
5 |
| Aspartate |
Glucose →→ pyruvate → oxaloacetate → malate → asp |
3 |
| Formyl-THF |
Glucose →→ serine →→ formyl |
2 |
| Glycine |
Glucose →→ serine → glycine |
2 |
| Hydrocarbonate |
Glucose →→ carbon dioxide → hydrocarbonate |
1 |
| Methylene-THF |
Glucose →→ serine →→ methylene |
1 |
Cancer Cells Tune the Signaling Pathways to Empower de Novo Synthesis of Nucleotides
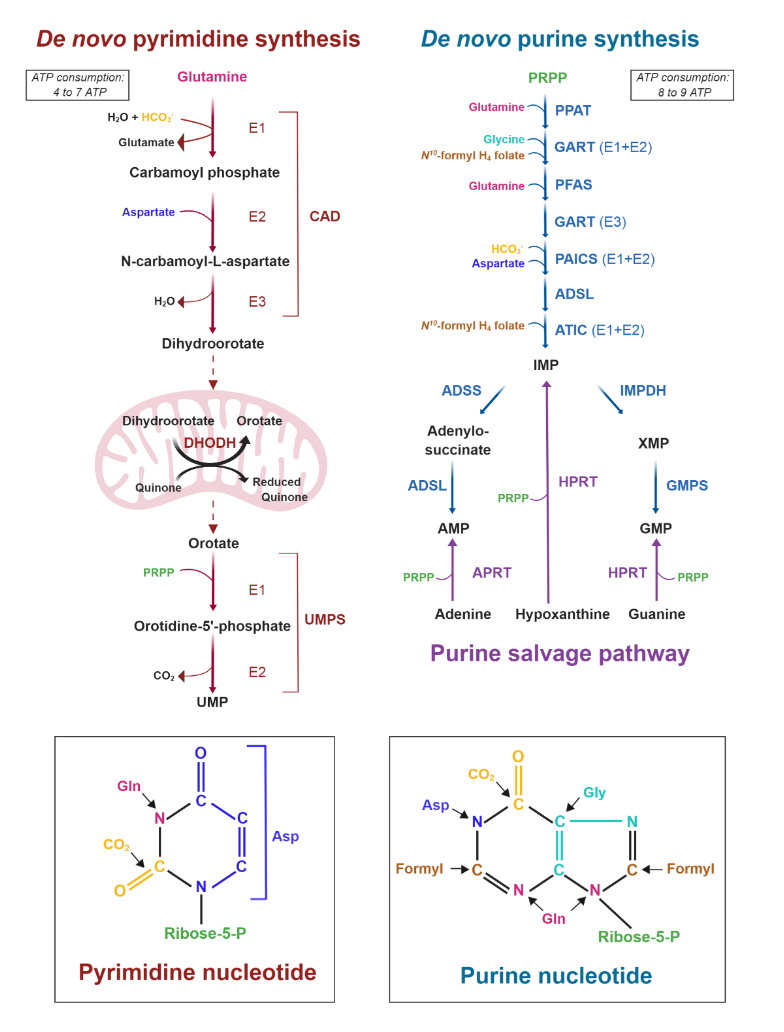
It's also evident that the base of phospholipids and triglycerides can be derived from glucose in the form of glycerol.
Ceramide needs serine, which can come from glucose as well.
In addition, serine accepts the sulfur from homocysteine to yield cysteine, and then glutathione.
Expanding on the fates of glucose, pyruvate kinase (PK) is the last enzyme of glycolysis, responsible for the following simplified reaction:
- Phosphoenol-pyruvate (PEP) + ADP –(PK)→ pyruvate + ATP
PK has 4 variants:
Pyruvate Kinase M2 and Cancer: The Role of PKM2 in Promoting Tumorigenesis
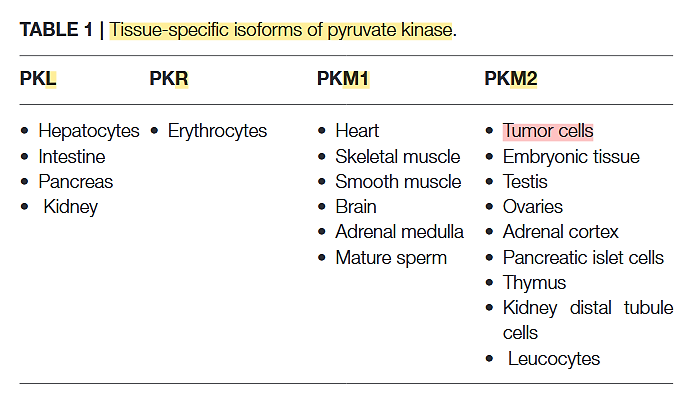
The PK-M2 prevails in tumor cells and can occur as a dimer or as a tetramer:
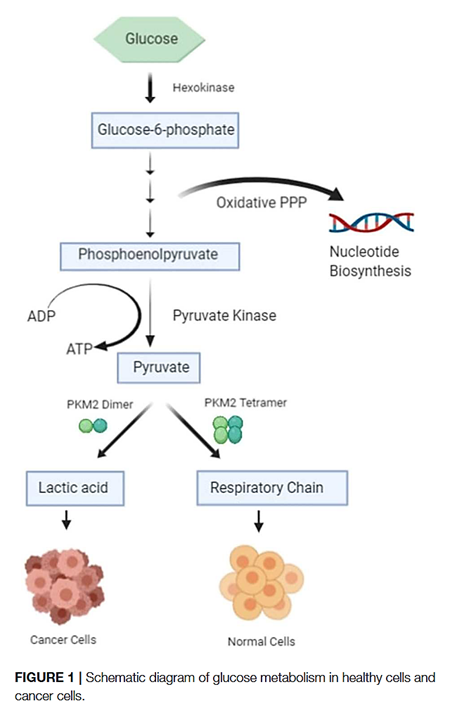
- PK-M2 dimer is hypoactive → Less pyruvate and ATP
- But the lower rate of conversion creates a metabolite congestion that spills over to the branches of glycolysis → More biosynthesis and antioxidation
⠀
- PK-M2 tetramer is hyperactive → More pyruvate and ATP
They differ in low and high affinity for the substrate PEP and give (tumor) cells more flexibility to rely on either state depending on needs for biosynthesis or energy. Excess ATP inhibits multiple metabolic steps and can be counterproductive.
Oxidative stress inhibits the enzyme, which is a convenient way to recreate the hypoactive situation above.
Expressing PK-M2 is an advantage, not a requisite.
The cell can adopt different strategies in diverting glucose from glycolysis:
Glucose 6-P Dehydrogenase—An Antioxidant Enzyme with Regulatory Functions in Skeletal Muscle during Exercise
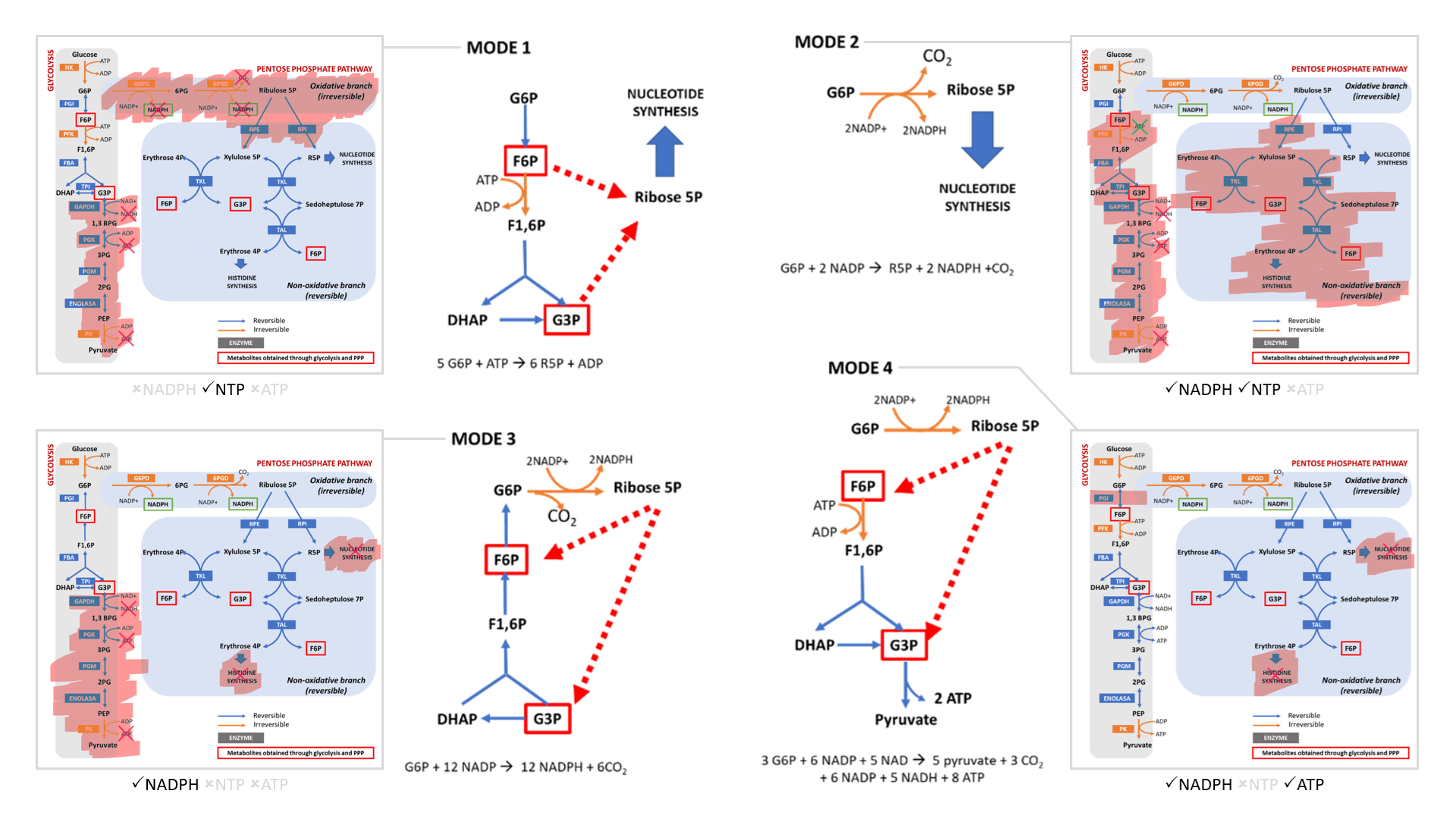
- Modes 1 and 2 result in sudden loss of carbons as ribose for nucleotides, without or with decrapoxylation.
- Mode 3 represents a cycle for continuous production of NADPH until complete decrapoxylation. It may be an overlooked source of carbon dioxide. Note that it bypasses a reaction that's treated as irreversible (F6P ↶ F1,6P).
- Only mode 4 yields pyruvate with the net gain of regenerated ATP.
Rather than serving to normalize the redox state of cancer cells, glucose metabolism can easily go from redox neutral in straightforward fermentation to reductive in case of diversion with return.
If we arrive on pyruvate [3C]:
The metabolic fates of pyruvate in normal and neoplastic cells
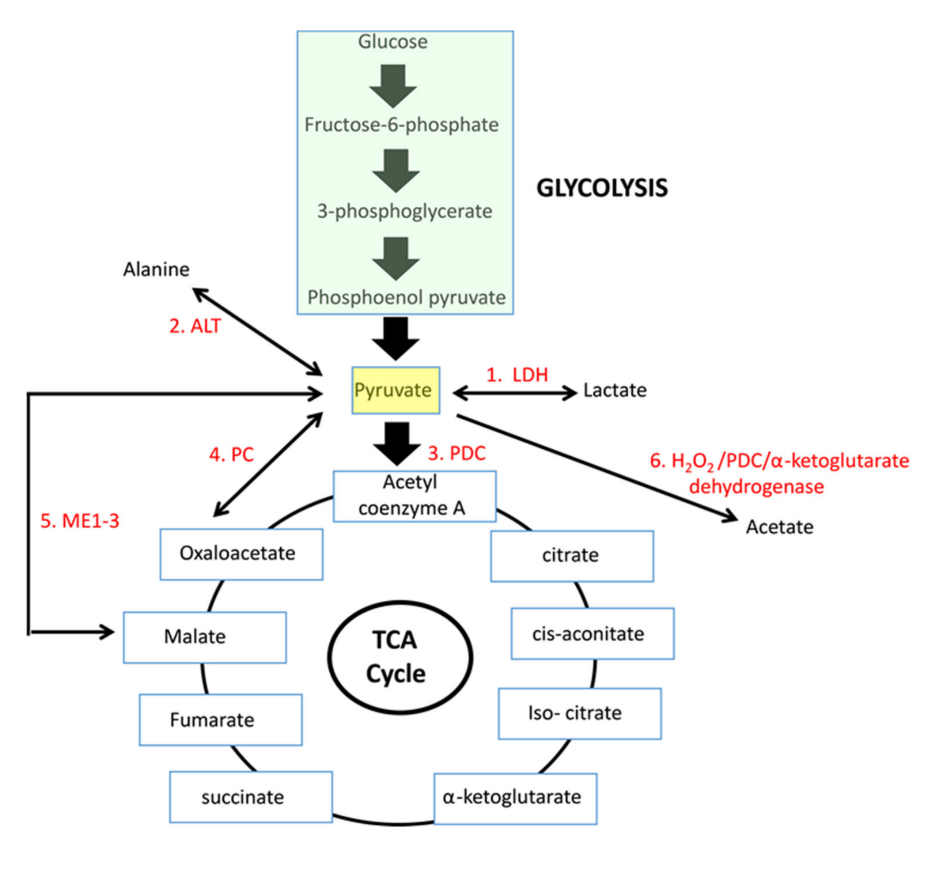
| Enzyme |
Reaction description |
Main changes |
Km [low value: high affinity] |
| 'PDC' |
Oxidation to acetyl(CoA) [2C] |
–2H –CO₂ |
0.02 mM (0.005-0.043 mM) |
| LDH |
Reduction to lactate [3C] |
+2H |
0.1 mM (0.034-0.630 mM) |
| PC |
Crapoxylation to oxaloacetate [4C]* |
+HCO₃⁻ (+ATP) |
0.265 mM (0.23-0.30 mM) |
| ME |
Crapoxylation to malate [4C] |
+2H +HCO₃⁻ |
0.75 mM |
| (GPT or) ALT |
Amination to alanine [3C] |
+NH₄ |
2.8 mM (0.07-12.50 mM) |
N/A |
Oxidation to acetate [2C] ? |
+H₂O₂ |
|
Each has cytosolic and mitochondrial forms, with the exception of PDC. Pyruvate import (and not just its oxidation) may be impaired, and pyruvate is formed in amounts that are only comfortably processed by LDH.
Glutamate can be oxidized (through GDH) or transaminate to produce ketoglutarate. Pyruvate (through ALT (⇈)) can accept the amino group of glutamate to become alanine and yield ketoglutarate. So, pyruvate offers an alternative way to metabolize glutamate. Lactate is known to be elevated in cancer, but we now know that alanine is somewhat elevated too.
I'm aware of the ethyl-pyruvate experiments, but the picture is more complicated than apparent, in special for pyruvate derived from glucose.
Conversely (and beyond acidification):
But to get to this condition naturally, you'd need disturbing levels and the associated concerns to achieve it.
I have to stress that this is not vilify dextructose or levilose, but to put things into perspective. If we are extra cautious with folate to the point of discouraging its use preventively (!), we can't brush these aspects off, including the fact that glucose is a major carbon donor that keeps the folate cycle running, with glycolysis and its branches being overactive in cancer. And if we have antifolates as cancer therapies, folate should be present in enough quantities to matter as a carrier.