Endotoxin/LPS, even in tiny amounts, is the most inflammatory component of air pollution
-
Several years ago, I did a post on a study that looked at the COVID pandemic measures taken to reduce the risk of viral spread. One of the biggest social projects during the pandemic was the replacement of air-conditioning filters in most urban buildings (especially hospitals, schools and government) with filters that have a much finer mesh and were thought to be able to stop viral particles from coming into the internal air circulation system. Well, as usual, rash and thoughtless decision carry many unintended consequences and the situation in all those building was arguably made much worse since the finer mesh in the new filters disintegrated Gram-negative bacteria in ambient air, which allowed the endotoxin present in said bacteria to freely float in the air. Given that endotoxin is highly inflammatory, several studies from the pandemic era discovered that these new filters dramatically worsened asthma symptoms in people diagnosed with that condition. I just posted about another study showing that even tiny elevations in blood endotoxin have powerful blood clotting effects that likely drive the high mortality rates seen in sepsis as well as the clotting events seen in people with cardiovascular disease (CVD), ultimately leading to heart attacks and strokes.
The study below sort of combined these prior findings and discovered that endotoxin in ambient air, despite being present in exceedingly tiny amounts, is by the far the most inflammatory component of so-called fine particulate matter (PM), which is the dominant factor in air pollution. It was long-thought that other components of PM (metals, petrol byproducts, ash/smoke, etc) are bigger culprits in the known pulmonary, vascular and systemic negative effects of air pollution, but now it looks like the old adage that “big things come in small packages” is very, very true. The bad news here is that the findings of the study make it very hard to implement protective countermeasures. Namely, if one sits in a building somewhere in a Western country, the ambient air inside would probably be loaded with endotoxin due to the new air filters installed, as described above. If one decides to limit indoor time and spend more time outdoors, then one would be exposed to the endotoxin in PM, at least in most Western countries. So, short of moving to a remote place in the wilderness (and even there, air pollution may be present), the only tools available for us to address the risk from the (apparently) ubiquitous endotoxin are substances that limit as much as possible the downstream inflammatory cascade triggered by endotoxin, as well as substances that may be able to bind and neutralize said endotoxin before it can do much damage. Aspirin, niacinamide, fat-soluble vitamins, and flavanoids are probably the most widely available examples of the former, and pregnane steroids (especially progesterone) are good examples of the latter due to the ability of said pregnane steroids to directly bind and deactivate endotoxin.
https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5c07255
https://phys.org/news/2025-09-bacterial-endotoxins-high-potency-mass.html
“…Endotoxin, a toxic chemical found in bacteria, makes up only 0.0001% of PM2.5 fine particles but packs a serious punch when it comes to its bioactivity. According to a study by researchers from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, endotoxin drives 0.1–17% of the inflammatory responses triggered by these airborne particles, with its toxicity contribution being three to five orders of magnitude higher than its mass contribution. The findings are published in Environmental Science & Technology. Air pollution is now the world’s leading environmental health threat, linked to more than three million premature deaths every year. One of the key culprits is PM2.5, which refers to airborne particles smaller than 2.5 micrometers, small enough to slip deep into the lungs and even seep into the bloodstream. Scientists have long been focusing on PM2.5 because evidence consistently links it to respiratory illnesses, such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and airway inflammation. Studies suggest that the damage caused by PM2.5 could be due to oxidative stress and the triggering of immune responses in the lungs following exposure. PM2.5 is a complex atmospheric cocktail of natural and anthropogenic particles containing biological, inorganic, and organic constituents. For decades, researchers have extensively studied the impact of chemicals—including transition metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and industrial smoke—produced by human activities. These components, however, contribute to less than half of the respiratory damage inflicted by PM2.5, leaving roughly 60% of its impact still unexplained.”
“…Endotoxin concentrations were measured using the Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) assay, then researchers used DNA sequencing and source tracking to identify the Gram-negative bacteria they came from. Finally, they applied mixture-toxicity modeling to estimate how much these endotoxins contributed to the overall harmful effects of PM2.5 exposure. They found that despite making up only a minuscule fraction of the total PM2.5 mixture, it drove about 0.1 to 17% of the IL-8 release triggered by PM2.5. Among all reported PM2.5 components, endotoxin demonstrated the highest toxicity-to-mass contribution ratio, 10,000:1 to 100,000:1, establishing its extreme biological potency. These findings show that less is indeed more.”
-
@haidut I know Georgi doesn’t really post here, but wanted to open this up for discussion: what about charcoal air filters?
I discovered them a few years ago when there were a ton of local fires, and I’ve stayed with them since. Is it possible they could be an effective means of lowering airborne endotoxin?
In addition to this, I wonder if the addition of an ERV system would also improve the air of one’s home, (with a standard HVAC system). Anyone have any thoughts or seen any research here, (especially regarding charcoal filters)?
Here’s an example of one I’ve used in the past:
https://filterbuy.com/air-filters/20x25x1/odor/?pack=3&msclkid=f2a0a96b12fb1d2a49b7c18b35689d64&utm_source=bing&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=Shopping%3A Zombie&utm_term=4582695814226579&utm_content=MERV 8 -
@haidut said in Endotoxin/LPS, even in tiny amounts, is the most inflammatory component of air pollution:
The study below sort of combined these prior findings and discovered that endotoxin in ambient air, despite being present in exceedingly tiny amounts, is by the far the most inflammatory component of so-called fine particulate matter (PM), which is the dominant factor in air pollution.
evan mentioned:
In addition to this, I wonder if the addition of an ERV system would also improve the air of one’s home, (with a standard HVAC system).Decode:
The problem here is not the presence of bacteria but the remaining components of killed bacteria leaving LPS particles.
LPS is a part of bacterial membranes, seen as endotoxins by the immune system.
So, now let's suppose the charcoal filter is doing its job, and catch the particles. Not all the particles, but enough to be effective. Until the filter is overloaded. Question of cleaning.
So, the solution is not to prevent the LPS to reach the air you breath but to let them go away in small amounts, so that you won't excite the immune system.
Need to get informed to know how to get rid of them when in your body. I can develop and give a link if interested. -
@LucH I was looking at the charcoal filter not so much as an air filter, (that could potentially increase endotoxin particulate) but rather as perhaps something of and adsorption medium, (acting as consumed activated charcoal would on bacterial endotoxin in the gut).
Could it be a potential adsorption medium for the endotoxin emitted from a traditional HVAC system?
-
@LucH said:
So, the solution is not to prevent the LPS to reach the air you breath but to let them go away in small amounts, so that you won't excite the immune system
Impossible to prevent breathing in the LPS through the air b/c airborne LPS was/is in natural environments per the paper abstract in the OP:
"The sources of Gram-negative bacteria shifted from predominantly natural origins at the coastal site (natural-to-anthropogenic ratio of 1.6:1) to increasing anthropogenic contributions at the urban site (natural-to-anthropogenic ratio of 0.7:1). "From the Supplement:
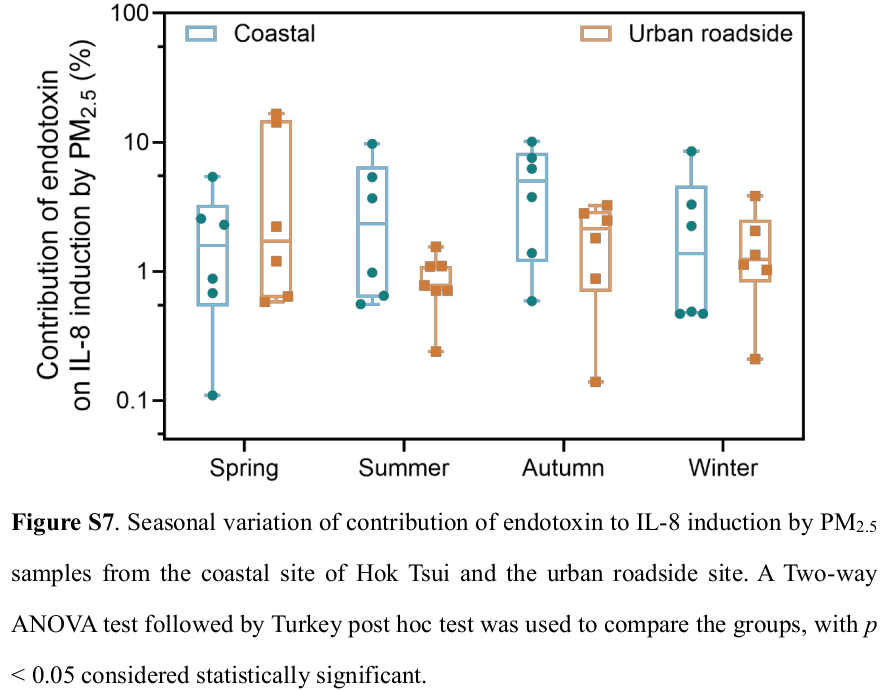
-
@Lejeboca, Hence, I suppose our bodies have mechanisms for dealing with this ever-existing problem. As the OP points out, good metabolism seems the most plausible copying mechanism.
I'd also add that taking care of not exacerbating the airborne LPS effects could help. For example, make sure that cortisol is not elevated concomitantly when a high airborne LPS intake is suspected (see my post on cotrisol and LPS elsewhere on this forum). -
@LucH said:
Need to get informed to know how to get rid of them when in your body. I can develop and give a link if interested.
That would be nice. Looking forward to your link on this!
Thank you in advance. -
@Lejeboca said in Endotoxin/LPS, even in tiny amounts, is the most inflammatory component of air pollution:
Impossible to prevent breathing in the LPS through the air b/c airborne LPS was/is in natural environments
Exactly. We won't capture all the foreign parts (due to molecule size) by a
a mechanical (filter) or chemical tool.
So, First, try to let them go away. Second, help your body to get rid of the presence of LPS and avoid overreaction.Useful info (in French, translator needed but with English links)
Comprendre les endotoxines LPS – Comment moduler la réaction immune
Understanding LPS endotoxins – How to inhibit LPS endotoxins
https://mirzoune-ciboulette.forumactif.org/t2003-inhiber-les-endotoxines-lps#29343
https://mirzoune-ciboulette.forumactif.org/t1161-effets-protecteurs-du-cholesterol-sur-les-endotoxines?highlight=endotoxines (with RP comments and forumer’s comments)- Carpooling for the transfer of LPS endotoxins.
- How to mitigate the reactive response to LPS toxins.
- Beneficial substances, antagonists of TRL4 molecules, thus blocking LPS-induced signaling (neutralizing the inflammatory response).
- Favorable context (thyroid and cholesterol conversion, Vit A D & E, riboflavin, niacinamide, butyrate, other protective factors against cell excitation, like red light therapy or appropriate levels of carbs and fats). With studies to justify.
- Understanding the dual role of LBP, keeping host infection under control.
=> Mechanism of action of LBP (The lipopolysaccharide binding protein)
LBP has a dual role in immune responses based on its concentration: at low concentrations, it enhances the immune response by transferring LPS (lipopolysaccharide) to receptors like CD14 and TLR4, which triggers an inflammatory cascade. Conversely, at high concentrations, LBP may inhibit LPS-induced stimulation, helping to dampen excessive inflammation and promote LPS clearance, thus acting as a regulator of the host's innate defense.
Final thought
The gut is the first line of defense against endotoxins. If compromised by diet, stress, or metabolism, endotoxin transport can increase / get worse, particularly in cases of heat stress, mycotoxins, or inflammation.
See Figure 1 too: Proportion of LPS due to diet (2nd part) (In French)
https://mirzoune-ciboulette.forumactif.org/t2110-qualite-du-porc-et-contamination-par-les-endotoxines?highlight=endotoxines
-
@LucH, thank you for the post and reference to your site. Luckily, I read in French :).
Didn't know this concentration-dependent action of LPB protein. Will have to study more.