L. Reuteri
-
@Amazoniac are you aware of any vitamins that L. reuteri consumes?
I only recall reading about it producing B12, but other than that I haven't come across anything like that. -
@Amazoniac interesting. Thank you much brother.
Funny, I’m quoting these old rpf threads to y'all, but y'all were in them lol @Mauritio
-
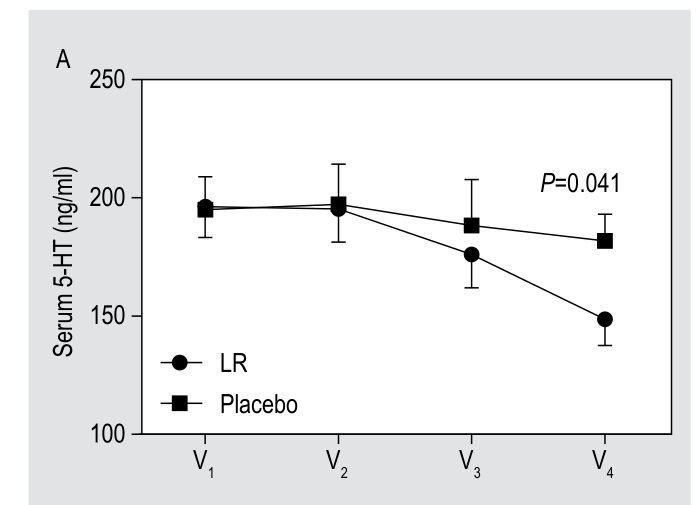
L. Reuteri 6475 potently increases the serotonin Transporter SERT, which picks up serotonin and thereby reduces its availability.
They also showed that it reduced colitis in a rat model and lowered inflammatory cytokines like IFNy or TNF.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34550056/
DSM 17938, the other strain in Bio Gaia's Gastrus, also decreases serotonin. In this case directly.
Interestingly the effect took a while to show,but after that inertia, the longer they took it the more it lowered serotonin.
-
@Mauritio have you increased your dose bud? (From a fourth of a tablet)
How much is everyone else taking? I know @Amazoniac is eating the yoghurt, is anyone else doing this too?
-
@Ismail yes I increased to 3/4 of a tablet and will increase further soon.
-
@Mauritio said in L. Reuteri:
@Amazoniac are you aware of any vitamins that L. reuteri consumes?
I only recall reading about it producing B12, but other than that I haven't come across anything like that.I don't, but it's something to consider if the person starts to notice negative effects. The problem is that the bacteria can't be considered in isolation, what matters is the result of its addition. L. reuteri might consume a vitamin, but promote the growth of producers that make up for it. Rate of production also matters: there can be substitution for consumers that use up little of it in relation to the previous colony. Competition is likely harsher between microbes than with the host. Therefore, if someone doesn't notice gut issues, gross depletions might not be a concern for this individual.
-
L. Reuteri is part of our historical gut microbiome. It has always been present in all mammals. In recent decades, it has become very hard to find in the human gut. The new normal is not to have reuteri present in our gut. It is thought that our modern lifestyle (highly processed foods, antibiotics, the over use of herbicide and pesticides, improved hygiene, chlorinated water) is the cause for this loss of diveristy in our microbiome.
Restoring reuteri is a hack for increasing our testosterone levels. It seems that it is simply restoring our testosterone levels in the direction to the levels to what they were for hundreds/thousands of years.
-
@Amazoniac I noticed some transient vitamin B2 and biotin deficiency symptoms.
Although I suspect that's more due to killing the bacteria that produce those vitamins via reuterin. -
In this study another L. Reuteri strain 36301, caused a Testosterone increase of about 250%, in males that is. In females it caused shinier hair and skin and no testosterone increase.
It also reduced weight gain during aging and the inflammatory cytokines TNFa .In the OP of this thread the testosterone increase was dependant on IL-10 , while in this study they did not find a difference in that marker, so there has to be another mechanism of action.
-
Results: In glucose-tolerant volunteers, daily administration of L. reuteri SD5865 increased glucose-stimulated GLP-1 and GLP-2 release by 76% (P < 0.01) and 43% (P < 0.01), respectively, compared with placebo, along with 49% higher insulin (P < 0.05) and 55% higher C-peptide secretion (P < 0.05). However, the intervention did not alter peripheral and hepatic insulin sensitivity, body mass, ectopic fat content, or circulating cytokines.
-
Kefir’s hidden gem: the health benefits of l. reuteri
Besides kefir, L. reuteri can also be found in other fermented foods, such as:
Sauerkraut
Kimchi
Kombucha
Miso -
L. Reuteri protects from ionizing radiation
L. Reuteri (KCTC 3594 and KCTC 3678) should help with acne via killing acne causing bacteria.
-
@AinmBeo
I made this yogurt. It’s mild, I like it
How much do you eat of it? Since I read about some concerns maybe I should just try it out first?Also, do you use the whey for anything specific?
-
@happyhanneke
I have 4 oz a day.
I dump the whey and lactic acid. -
Tryptophan can go down the kynurenine, pathway, the serotonin pathway or the indole pathway.
L . Reuteri increases Tryptophan metabolism into the indole pathway, which lowers its availability for the serotonin pathway.
Not only that, the metabolites of this specific pathway have anti-inflammatory effects. They treat experimental colitis.
One even acts on the pro-metabolic PXR , similarly to pregnenolone or progesterone."As expected, the expression of Pxr (also known as Nr1i2), a receptor for IPA [41], and PXR target genes Ugt1a1 and Cyp3a11 increased markedly in the colon of DSS-treated mice in response to L. reuteri (Fig. 1E)."
-
@Mauritio I have a lot of thoughts about these results because what if actually milk. Most people take L. Reuteri through yogurt, so...maybe milk is more responsible than the strain.
Also, in the case where someone takes a probiotic pill with it in there, what is the difference between people who consume dairy alongside it or across the day versus people who don't...
I took homemade L. Reuteri yogurt before peating while on carnivore. It didn't really improve much for me during that time. I enjoyed eating it though in comparison to all the meat that I was eating.
-
L. Reuteri increases Vitamin D. Maybe by increasing cholesterol conversion into vitamin D since it also lowers cholesterol.
"L. reuteri NCIMB 30242 increased serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D by 14.9 nmol/L, or 25.5%, over the intervention period, which was a significant mean change relative to placebo of 17.1 nmol/L, or 22.4%, respectively (P = .003)."
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23609838/ -
Beneficial bacteria inhibit cachexia
Muscle wasting, known as cachexia, is a debilitating condition associated with chronic inflammation such as during cancer. Beneficial microbes have been shown to optimize systemic inflammatory tone during good health; however, interactions between microbes and host immunity in the context of cachexia are incompletely understood. Here we use mouse models to test roles for bacteria in muscle wasting syndromes. We find that feeding of a human commensal microbe, Lactobacillus reuteri, to mice is sufficient to lower systemic indices of inflammation and inhibit cachexia.
-
 J jhp referenced this topic on
J jhp referenced this topic on
-
 D DavidPS referenced this topic on
D DavidPS referenced this topic on
-
I assume the added inulin is mainly meant to help build the consistency of the product. As a sort of thickener.
I had seen that some people use (potato) starch instead of inulin in their L. reuteri recipes.Having had neither potato starch nor inulin at home I just threw a tablespoon of dextrose at my mixture, so that the reuteri won't run out of nutrients (the natural lactose content).
Accidentally, whilst looking for GABA-producing microbacteria (L. reuteri does not contribute, the small amount it produces merely helps its acid resistance. But it feeds of glutamine for that, much more than off glutamate),
I discovered that L. reuteri strain LGM (most similar to WHH1689) does not even eat inulin!
(see "LR" in table C below)
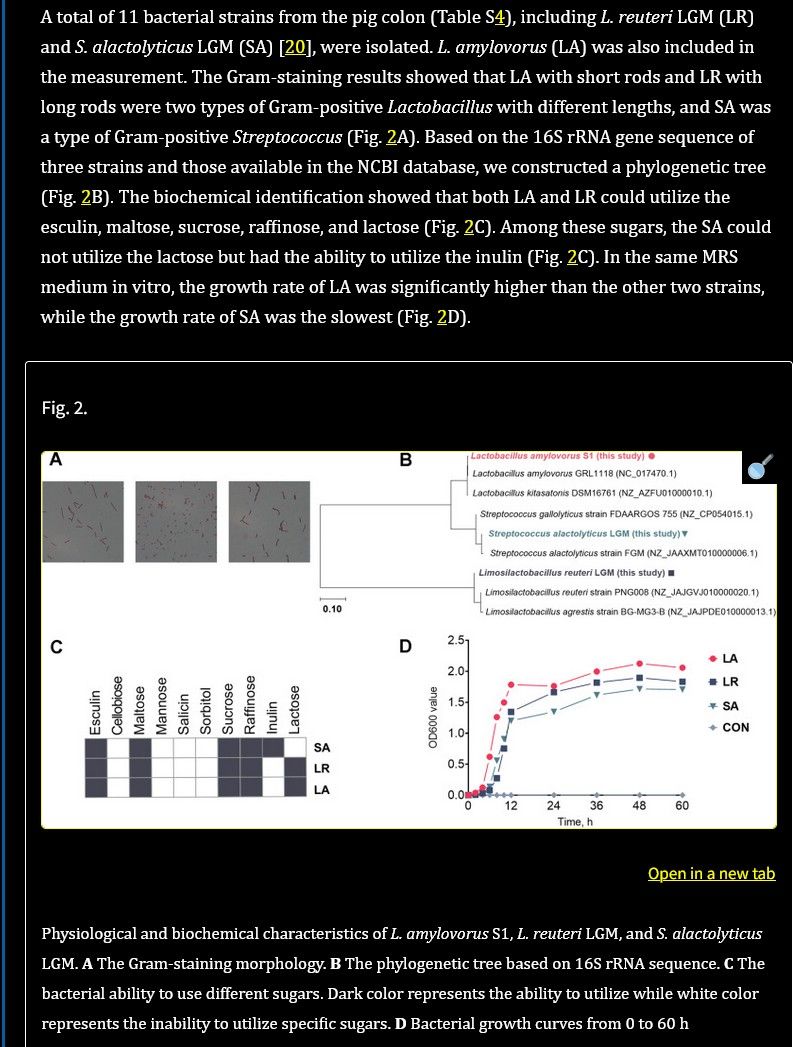
Regulation of serotonin production by specific microbes from piglet gut
So what's behind that story of adding inulin to feed the reuteri?
It seems to be untrue. The added inulin will feed other commensal bacteria, perhaps already in the fermentation batch, definitely once in the gut - yet it's seemingly no substrate for reuteri!
In fact, L. reuteri expresses inulosucrase as an enzyme which converts sucrose (saccharose, i.e. table sugar) to inulin, which other bacteria may then feed off.Wouldn't it then be better to add lactose, sucrose or maltose to L. reuteri recipes?
And just be honest about inulin acting not as a substrate for reuteri but on its own as a prebiotic on other bacteria as well as helping with consistency?
Or are there such drastic differences between the L. reuteri strains that ATCC PTA 6475 is able to feed off inulin? -
@CrumblingCookie I've been making L. Reuteri yogurt without the inulin or any other added prebiotic and it comes out great. I also make some batches with raw milk and it tastes just the same as the batches where I heat the milk. I'm not sure why people heat the milk to 180 F for 30 minutes. Bringing it up to 165 F for 15 seconds should be good enough to kill competing bacteria, 180 F for 10 denatures the protein and makes it set thicker, though my raw milk gets thick enough. I use goats milk.