Thymus health
-
Anyone tried thymus extract / Thymosin? Some studies showed strong anabolic and immune-promoting effects; it seems to have been a popular "pharmaceutical" treatment back when doctors had spines (and functioning thymus glands?!)
-
@DavidPS said in Thymus health:
I am waiting for the results of the TRIIM-X trial (Thymus Regeneration, Immunorestoration and Insulin Mitigation) mentioned in this paper.
When there is a lack of T cells in the body, it can lead to immunodeficiency diseases. Your thymus is the source of new T-cell specificities that fight infections, autoimmune cells and cancer.
This to make the junction with mTOR pathway.
Regulation of T-cells by m-TOR
doi: 10.1016/j.it.2014.11.005
How does mTOR affect T cells?
Overall, by functioning as a central hub that coordinates multiple signaling pathways, mTOR plays a critical role in regulating various aspects of T-cell function, including T-cell development, activation, differentiation, migration, survival, memory formation, and exhaustion.
I can develop but it's going to be a bit too long ...
Well, without giving the details, I use H3CO2 (bicarbonate 2 g) to reset the system from time to time (seasonal).
In the case of chronic inflammation, induced by overexpression of the immune system, the researchers found that the ingestion of H3CO2 (2 g bicarbonate) made it possible to restore normal Treg function so that these cells can do their job(s), and temper self-reactive T cells that attack one's own organs in autoimmune diseases.
NB: In cure, of course. Do not stay too long in M2 mode. Alternate balance is required.
I can develop but not in this post. Too long and I don't want interferences with the_one_I_can_not_mention_the_name
-
@LucH - I will try using H3CO2 to reset my system.
-
-
@Lejeboca said in Thymus health:
This got me thinking that, since our endogenous CORT is "naturally" elevated in the morning, if we have an LPS-prone breakfast, then any existing inflammation will spike.
So- rule #1, breakfast that is easy on digestion (Ray-Peat-right-again!)
At breakfast time consider - charcoal or anything digestion-promoting
- getting red/sun light at breakfast time to to decrease NO and other inflammatory cascade factors.
Thanks. What would tou consider to be an LPS-prone breakfast? Is it a soluble fiber-rich breakfast, one that includes substances that kill bacteria and thus produce LPS remnants of bacteria? What are some noteworthy examples of such a breakfast?
- rule #1, breakfast that is easy on digestion (Ray-Peat-right-again!)
-
@T-3 said in Thymus health:
What does "M2 mode" refer to?
Repolarization of macrophages M1 <> M2
Lymphocyte T polarization
In an (over-simplified) model, the Th1/Th2 and M1/M2 ratios (M=macrophages) can thus be used as indicators to determine whether or not the immune system is in M1/inhibitory type mode, oriented towards host defense, or in an M2/healing type mode, oriented towards the repair and replacement of lost or defective tissues with a view to maintaining host homeostasis. (Mills 2015a).
(doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00059)
Vocabulary:
M stands for macrophage
Th stands for thymus. Th1 = T helper cell type 1, produced by thymus. = lymphocyte, a type of white blood cell.There are two major types of T cells: the helper T cell and the cytotoxic T cell. As the names suggest helper T cells 'help' other cells of the immune system, whilst cytotoxic T cells kill virally infected cells and tumors.
Treg cells
Regulatory T cells, or Tregs, are white blood cells that play a key role in regulating your immune system. Tregs control your body's immune response to keep it from over-reacting to harmful invaders known as antigens. Antigens are frequently unwelcome substances that cause an immune response in your body.Understanding macrophage cells and the balance to find between M1 & M2, inducing a TH1 or Th2 answer (by Treg cells). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4329822/
-
@yerrag said in Thymus health:
What would tou consider to be an LPS-prone breakfast? Is it a soluble fiber-rich breakfast, one that includes substances that kill bacteria and thus produce LPS remnants of bacteria? What are some noteworthy examples of such a breakfast?
Oops. Missed your question, almost a year-old by now.
I'd say, anything that will sit/rot in your stomach long to let bacteria rejoice and produce LPS.
In my past life, I used to have beans for breakfast when travelling in Ireland. -
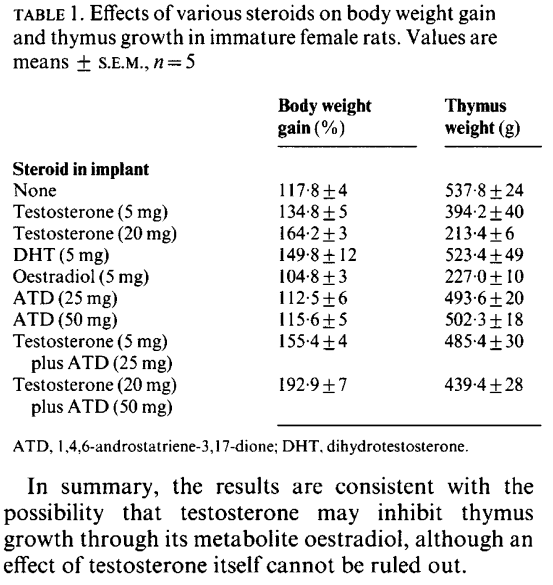
A hormonal take on thymus:
Estrogen Blocks Early T Cell Development in the Thymus
From RESULTS:
- Estrogen treatment caused a dramatic reduction in thymic size and cellularity. Implantation of slow release estradiol and estriol pellets lead to a marked reduction in total thymic cell recovery after 2 weeks.
- Progesterone alone had no effect on thymic cell counts, while progesterone when given with estrogen had a synergistic effect.
- We did not observe any significant difference in the total cell recovery between
control sham operated and ovariectomized mice ([part of] Table I):
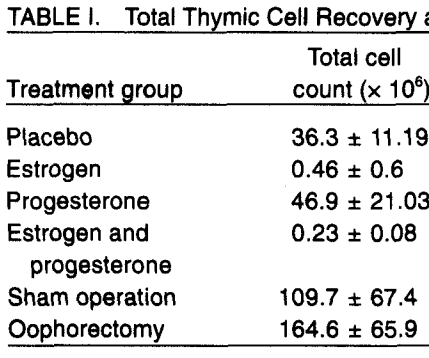
From DISCUSSION:
- Estrogens probably affect the thymocytes both directly via estrogen receptors and indirectly by causing a reduction in the bone marrow precursor cells. Estrogen and progesterone receptors have been identified in thymic tissue [5-7], supporting the concept that sex hormones can regulate immune function through the thymus.
-
@Lejeboca Thanks. Much in line with what we think of soluble fiber rich foods. Makes me think of going back to juicing, as that takes a lot of soluble fiber out of eating fruits, which while potassium rich almost always, if not always, comes with the baggage of soluble fiber.
-
Syringic acid for thymus health
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39383831/ -
@Mauritio said in Thymus health:
@cs3000 said in Thymus health:
another one, 6% protein calories vs 20%
4 calories in 1 gram of protein
at 2500 calories human equiv ~35grams daily gave a way smaller thymus vs 125grams protein daily with extra carbs replacing the lost protein,87% lower thymus weight from 35g protein
Not sure how to make sense of the above two statements . Other than low protein seems to be more detrimental than FGF21 os beneficial for thymus health.
-
-
@TexugoDoMel awesome. Thanks for sharing !
-
-
The thymus can produce pregnenolone and cortisol. Similarly to the andrenal glands.
Just haven't found info on how significant this hormone production is. -
@Mauritio
the fgf21 is largely through mtor , (rapamycin abolished effect)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39972173/
still hindered when on low protein with the increase so yeah guess its weaker more of a support (when they knocked out fgf21 in the young mice in study you posted their thymocyte numbers didnt change). something can happen in aging with mtor signalling still high but fails to create anabolic response i guess need boththis one affected thymus of young mice sort of, in some composition changes. and showed fgf21 is maintained high in thymus regardless of regular eating (protein intake)
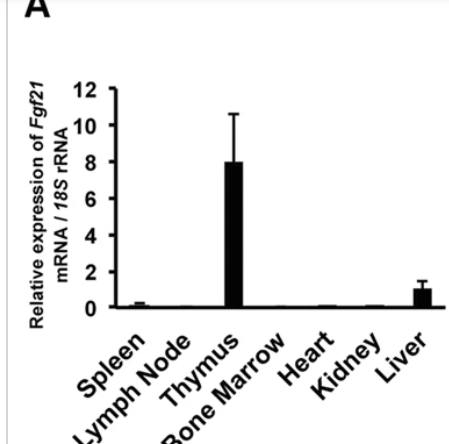
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-00349-8
(also a bit in the liver , because these 2 are always vulnerable needing protection & to regenerate more & more often)Its a pretty wide comparison , i'd guess ~60g protein wouldnt show a loss. or adding some leucine
@cs3000 said in Thymus health:
~35grams daily gave a way smaller thymus vs 125grams protein daily with extra carbs replacing the lost protein,87% lower thymus weight from 35g protein
Not sure how to make sense of the above two statements . Other than low protein seems to be more detrimental than FGF21 os beneficial for thymus health.
-
@cs3000 said in Thymus health:
the fgf21 is largely through mtor , (rapamycin abolished effect)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39972173/
still hindered when on low protein with the increase so yeah guess its weaker more of a support (when they knocked out fgf21 in the young mice in study you posted their thymocyte numbers didnt change). something can happen in aging with mtor signalling still high but fails to create anabolic response i guess need boththis one affected thymus of young mice sort of, in some composition changes. and showed fgf21 is maintained high in thymus regardless of regular eating (protein intake)
Makes sense!
It seems that FGF21 can up or down regulate mtor depending on tissues.In this study FGF21 lowered mtor in the liver
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26926384/And in this study in cancer cells it lowered it as well.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7985321And the strong expression of FGF21 in thymus tissue is a brilliant adaption of the body to a low protein diet. Since low protein weakens immunity via lowered mtor, but it strongly increases FGF21 in thymus which activates mtor locally and improves immunity.
But it's wild how big the difference in FGF21 is between different tissues! Nothing comes close to the thymus.
-
10-HDA from Royal jelly restores thymus health in immunosuppressed mice.
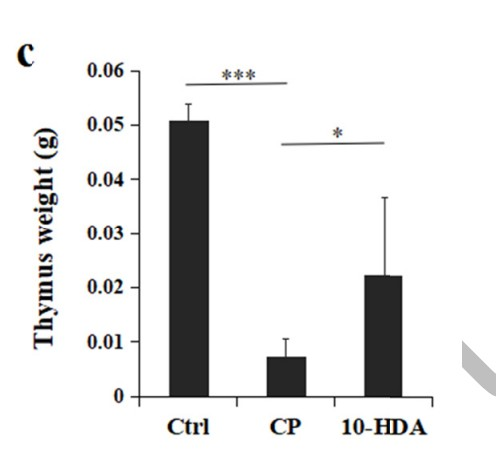
Dosage was quite high . HED~ 30-60g
-
The negative effects of androgens on thymus health, Sometimes observed, are medicated through the Glucocorticoids receptor.
Maybe aromatization of testosterone,/ estrogen activates it."The androgen-induced thymic involution was dependent on GC action, because this was completely absent in mice lacking GC receptor (GR) expression specifically in thymocytes. We provide here an unrecognized mechanism how androgens contribute to thymic involution by stimulating local synthesis and release of GCs in the thymus."
-
@TexugoDoMel, thanks for the tables. Interesting, indeed.
Do you have a reference paper for the tables?