A combination of vitamin B1/B3/B7 and aspirin, has curative effects on human mantle-cell lymphoma
-
@Ismail Final update on this topic...
As promised above, I ran it for about another 30 days. So I did it from May 18 2024 through Aug 24 2024 which is 98 days. I then stepped down dosages over 8 days. I have continued with a daily baby aspirin (81mg) but otherwise the protocol is finished.
The benefits I noted in an earlier post remained through the end of the experiment. I don't believe I posted on this "benefit" but my alcohol tolerance was through the roof and I had no brain fog or other hangover the next day. I don't drink a lot anymore and usually limit myself to 1 or 2 drinks in a whole week; if I do 2 drinks at once I get a hangover. This protocol cured that.
Once I quit the protocol, my energy levels settled at a lower level again. My breathlessness on stair climbs also returned. My alcohol tolerance is worse than it's ever been, so other than a glass of wine once a week with my wife I don't even drink anymore. My favorite cocktails (sidecar, manhattan, gin martini) now make me feel terrible after just 1 of them.
I wish I had better news. At minimum, I'll say this protocol was safe for me but I see little reason to try it again any time soon.
-
Hey guys, someone dear to me was recently diagnosed with pancreatic cancer. It's pretty severe with few options moving forward, so I'm going to give this b vitamin and aspirin protocol a try for her. I'm also thinking doxycycline, RU486, baking soda, and vitamin D, and maybe Progest-e and thyroid. Throwing everything at it.
Just wondering if anyone has experimented with this and had any insights overall. I don't want to overload her with a ton of things and cause more stress, but these all seem to be good ideas based on what I've learned here. Any thoughts would be greatly appreciated. Thank you.
-
We know from Ray and other authors that thiamin, niacin, and aspirin have therapeutic potential in cancer. It seems that biotin was included in the combination without much consideration, and Jorge had access to more promising options already in his store.
I know that the priority is to nourish the person, but it's most effective when we limit nourishment to cancer cells. Biotin is a vitamin whose anabolic functions prevail, making supplementation a questionable intervention.
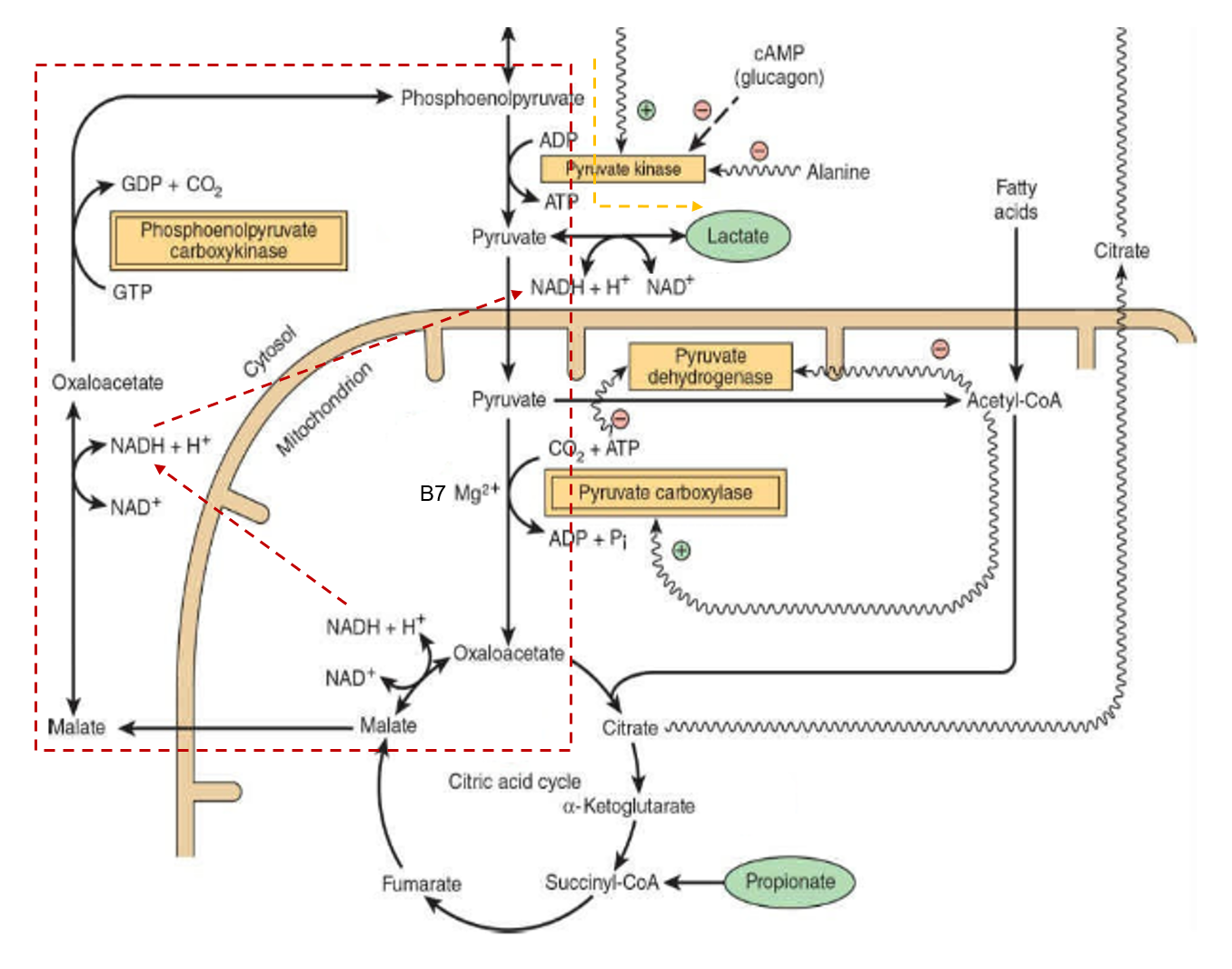
The assumption might have been that if pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) is inhibited, the alternative means to metabolize pyruvate away from lactate would be with the biotin-dependent pyruvate carboxylase (PC) to oxaloacetate.
Mitochondria are not just energy-producing organelles, they're also biosynthetic sites, with pyruvate carboxylase having an important role in this anabolic picture.
Oxaloacetate can help to export excess mitochondrial acetyl-CoA (that reinforces PDH inhibition and stimulates PC). This acetyl-CoA can then be used to synthesize fats in the cytosol, a process that's started by acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC)--another biotin-dependent enzyme.
Roles of pyruvate carboxylase in human diseases: from diabetes to cancers and infection
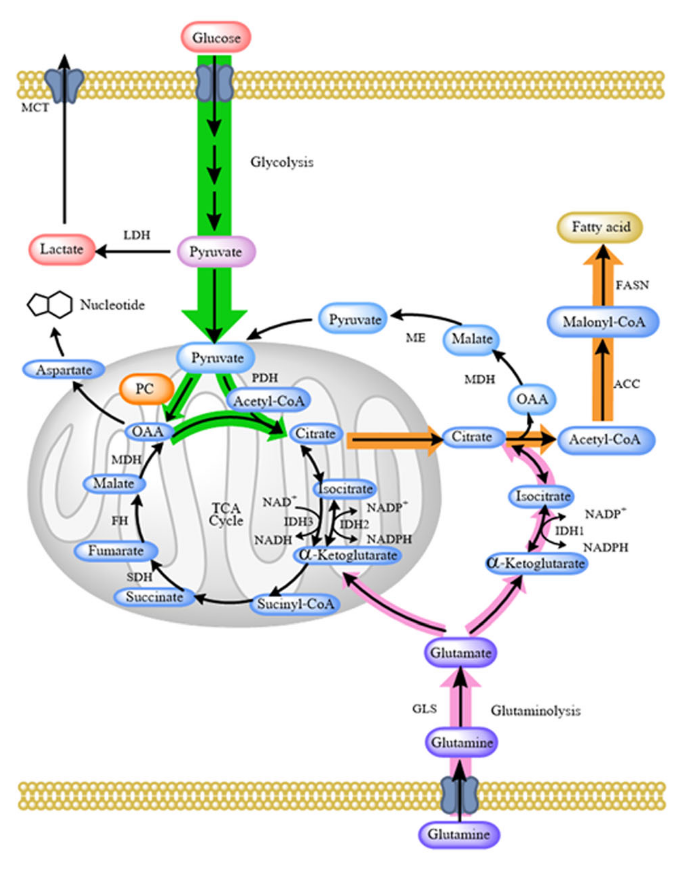
Yes, PC-derived oxaloacetate can refill the TCA cycle, but so does ketoglutarate from glutamate or glutamine, and they can cooperate.
Two other biotin-dependent enzymes (MCC and PCC) are involved in amino acid metabolism and can also channel the products to refill the cycle. These products would enter the TCA cycle right where ATP is synthesized through substrate-level phosphorylation (Tommy), with higher chances of bypassing inhibitions.
Therefore, all 4 biotin enzymes can converge in anabolic processes that may be problematic in the context of cancer.
To compound the concerns, simple conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate is one step away from aspartate synthesis, needed for the upregulated nucleotide synthesis.
This aspartate can also participate in the malate-aspartate shuttle, that serves to import cytosolic NADH. Normally, oxalate is formed from malate, but if this is reversed with the help of pyruvate carboxylase, the shuttle could perhaps work in reverse, and it would contribute to the export of NADH, with higher cytosolic NADH/NAD⁺ promoting lactate synthesis. In addition, it can be an alternative way to regenerate NAD⁺ when respiratory complexes are compromised, to allow the TCA cycle to keep functioning.
In fairness, some of these processes concentrate in liver and kidneys, and biotin may also relieve the burden in supporting clearance of excess lactate from cancerous tissues (lactate → pyruvate –B7→ oxaloacetate → pyruvate enolphosphate →→ glucose), possibly more so than thiamin, as local pyruvate oxidation without redistribution as glucose could perhaps overwhelm such organs. However, thiamin could be of better service for other tissues, that clear lactate through complete oxidation.
Even in cases where biotin supplementation normalizes glucose metabolism, the anabolic component can't be discarded.
Some Aspects of Carbohydrates Metabolism in Biotin-Deficient Rats
"It is possible, therefore, that these changes in the fatty acid composition of the lipid might alter the structural integrity of mitochondria with the consequent effect on oxidative phosphorylation. This defect, as reflected by amino acid incorporation studies, was compensated during early stages of the deficiency when the animals received an oxidizable substrate such as succinate (see reference 1) or fructose or sorbitol in the basal diet. It is, therefore, possible that a moderate decrease in oxidative phosphorylation does not limit the efficiency of the biotin-deficient animal as long as adequate levels of oxidizable substrates are maintained. However, in advanced deficiency as observed after 8 weeks on the deficient diet, succinate, sorbitol, or fructose feeding did not help the animal. Only administration of biotin restwed fatty acid synthesis and the integrity of mitochondria for normal oxidative phosphorylation."
It's no wonder that symptoms of biotin deficiency point to anabolic defects, such as disturbed skin lipids.
I would be careful with its supplementation in advanced cancer and observe reactions. It's preferable to avoid B-vitamins formulas and have the vitamins separately for better control.
This is not to suggest that thiamin, niacin, and aspirin are entirely beneficial in cancer because they're not, but their positive outweigh negative effects. Biotin isn't invariably problematic, but seems riskier.
-
@max anything to update on this? also https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6051000/ https://bioenergetic.forum/post/22196
-
To reinforce, the bright side of biotin is unlikely to be in diverting pyruvate away from lactate when its oxidation is inhibited, but in helping to process this lactate once it's taken up by normal cells.
For an idea of the extent of lactate production:
Lactate Metabolism in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
"Using an isotope tracer technique, we found increased rates of lactate production in 20 patients with metastatic colorectal cancer [Ca] compared to 13 control subjects [C] of comparable age and sex (15.6 ± 1.3 μmol/kg/min versus 10.4 ± 0.6 μmol/kg/min; p < 0.01)."
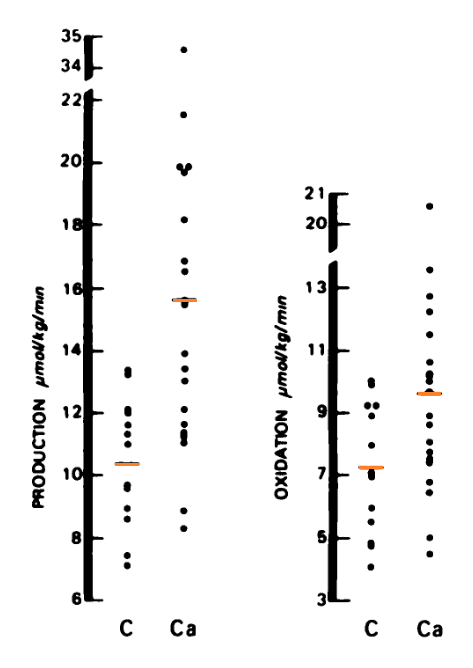
Their most extreme case produced lactate at 34.5 μmol/kg/min (3.48 mol/70 kg/24 h).
2 lactates per 1 glucose:
- 3.48 ÷ 2 → 1.74 mol/70 kg/24 h
Unit conversion:
- 1.74
mol/70 kg/24 h × 180 g/mol= 313 g/70 kg/24 h
They discount the typical production based on the control group, which was 10.4 μmol/kg/min (1.05 mol/70 kg/24 h):
- 1.05 ÷ 2 → 0.53 mol/70 kg/24 h
Unit conversion again:
- 0.53
mol/70 kg/24 h × 180 g/mol= 95 g/70 kg/24 h
The difference:
- 313 – 95 = 218 g lactate/70 kg/24 h
However, lactate must not be a burden to normal tissues if it's widely distributed and metabolized oxidatively, because it's the catabolism of glucose continued elsewhere (glucose →→ pyruvate
→ lactate → pyruvate→→ carbon dioxide + water)."When control subjects were compared to the cancer patients, no significant difference was observed in the percentage of CO2 derived from lactate oxidation (21 ± 1.6 versus 25.3 ± 1.7%)."
"The percentage of the lactate production which was immediately oxidized was not related to the rate of lactate production, the mean values in the control subjects and cancer patients being 68.3 ± 2.7 and 62.1 ± 2.4%, respectively.
"Lactate disposal by mechanisms other than immediate oxidation, i.e., the difference between the lactate production rate and the oxidation rate, was significantly increased (p < 0.001) in the cancer patients (227 ± 24 versus 128 ± 8 μmol/sq m/min or 6.0 ± 0.7 versus 3.2 ± 0.3 μmol/kg/min)."
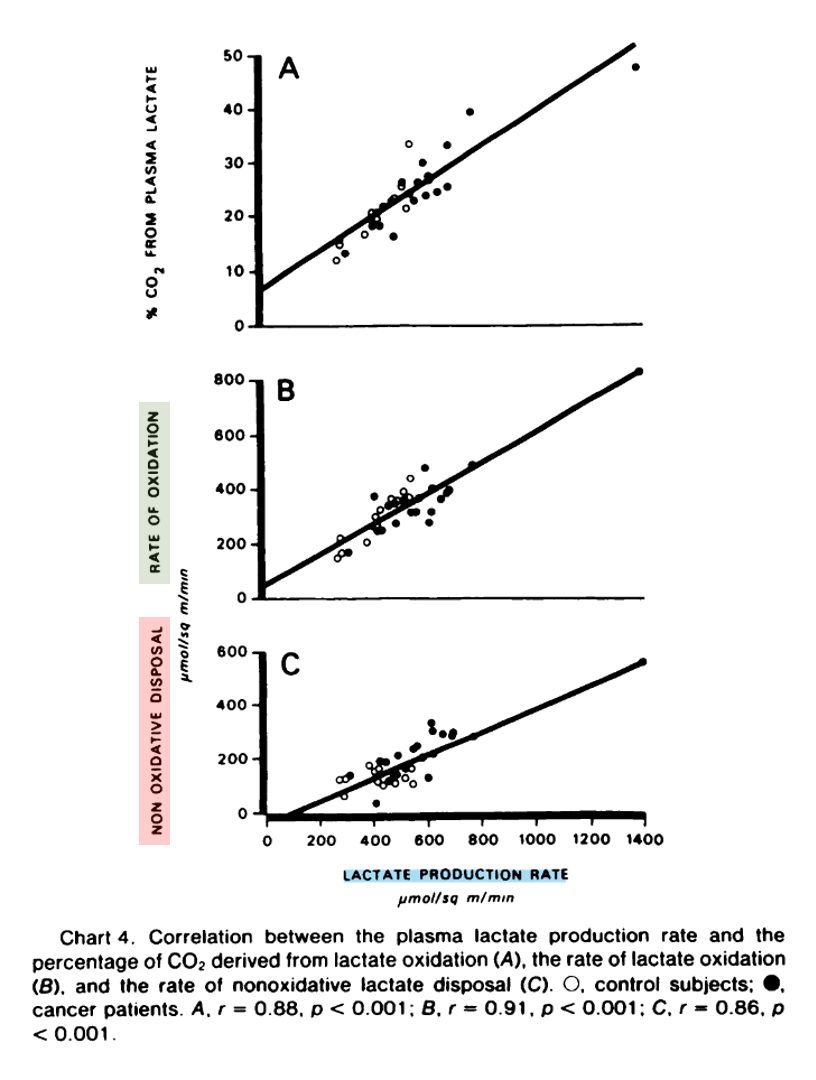
"The rate of nonoxidative lactate disposal was directly related to the lactate production rate (Chart 4). At least in part, conversion of lactate to glucose may account for the greater difference observed in the nonoxidative disposal in cancer patients in whom the percentage of glucose derived from lactate was significantly increased, (23.1 versus 15.8 ± 1.7%; p < 0.01). The percentage of glucose derived from lactate was also directly related to the lactate production rate (Chart 5)."
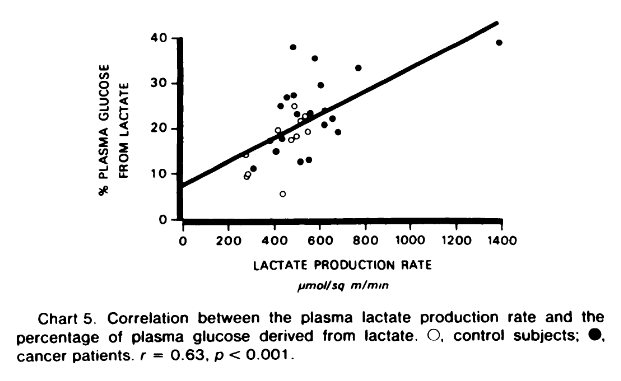
The burden comes when lactate reforms glucose, which occurs concentrated in specific organs. Not only the synthesis of glucose from lactate consumes more energy (–6ATP) than is produced (+2ATP) in the partial breakdown of glucose, but the energy produced may be left behind where breakdown occurred, making the site of clearance an exclusive energy consumer. Yet, the body has the option to oxidize it at any time in place of glucose to avoid ATP shortage.
But an additional concern is that glycogen is found in cancer cells as well, giving them metabolic independence to maintain activity when nutrients are scarce.
Cells go through cycles of depletion and repletion, and with excess lactate around, it's possible that part of it is channeled to glycogen synthesis. Therefore, we have to wonder where glucose resynthesis (through pyruvate carboxylase) is desirable.
An assumption is that tumor lactate stems only from cancer cells, but it can be formed in surrounding cells (fibroblasts or macrophages, for example) and cancer cells may exploit it to their advantage, whether in oxidizing it or as speculated above. It's also possible to have neighboring cancer cells fermenting and respiring in cooperation.
This adds a layer of complication in trying to explain the benefit of nutrient supplementation with a focus on local metabolism.
-
Glycolysis can be reversed starting from different molecules, and PC-derived oxaloacetate is one of the ways. Reverse glycolysis doesn't have to end on glucose (or glycogen) either, reversal can be partial to get to the branching points, as an alternative means to yield products needed for biosynthesis.
The issue relates to the carefree thiamin supplementation. Enthusiasts treat it as if it could only serve to disinhibit pyruvate dehydrogenase as intended, but it's not the case.
B Vitamins and Their Role in Immune Regulation and Cancer
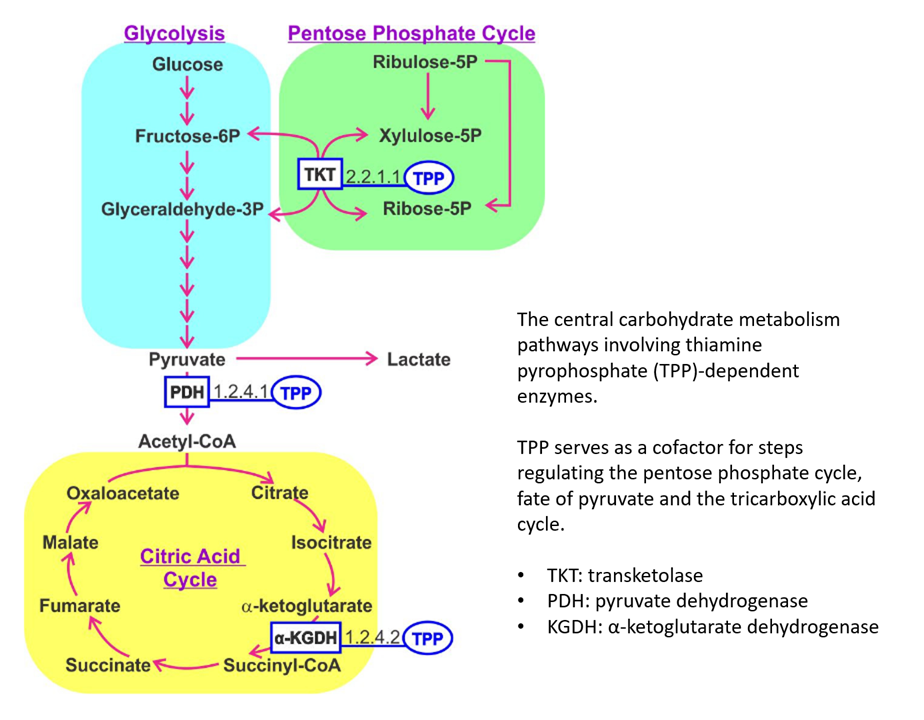
TKT and KGDH can be overactive, whereas PDH underactive in cancer. Additional thiamin would be in favor of the ongoing activity of TKT and KGDH, while going against the inhibition of PDH.
- Role of Thiamin (Vitamin B-1) and Transketolase in Tumor Cell Proliferation
- Thiamine supplementation to cancer patients: A double edged sword
For thiamin to get to mitochondria, it must first pass through the cytosol, where it's activated to thiamin diphosphate. Depending on the exact site of activation, TKT is cytosolic and may have privileged access to extra thiamin.
Linking vitamin B1 with cancer cell metabolism
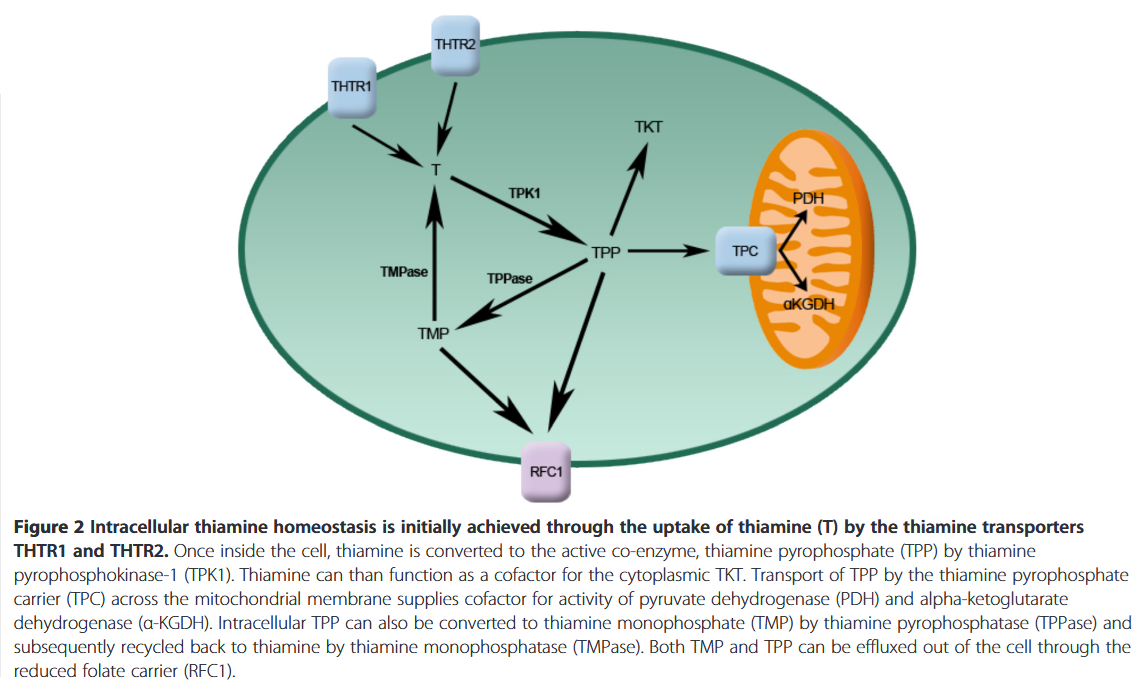
If thiamin reaches mitochondria in therapeutic amounts, PDH must compete with KGDH for it, and PDH is more susceptible to regulation and inhibition than KGDH. Even with proper amounts of active thiamin, PDH may remain inhibited as a consequence of other controlling factors. And the TCA cycle (with KDGH) can be running independently of PDH. For example, with acetyl groups from fatty acids and ketoglutarate from glutamate.
Consider this:
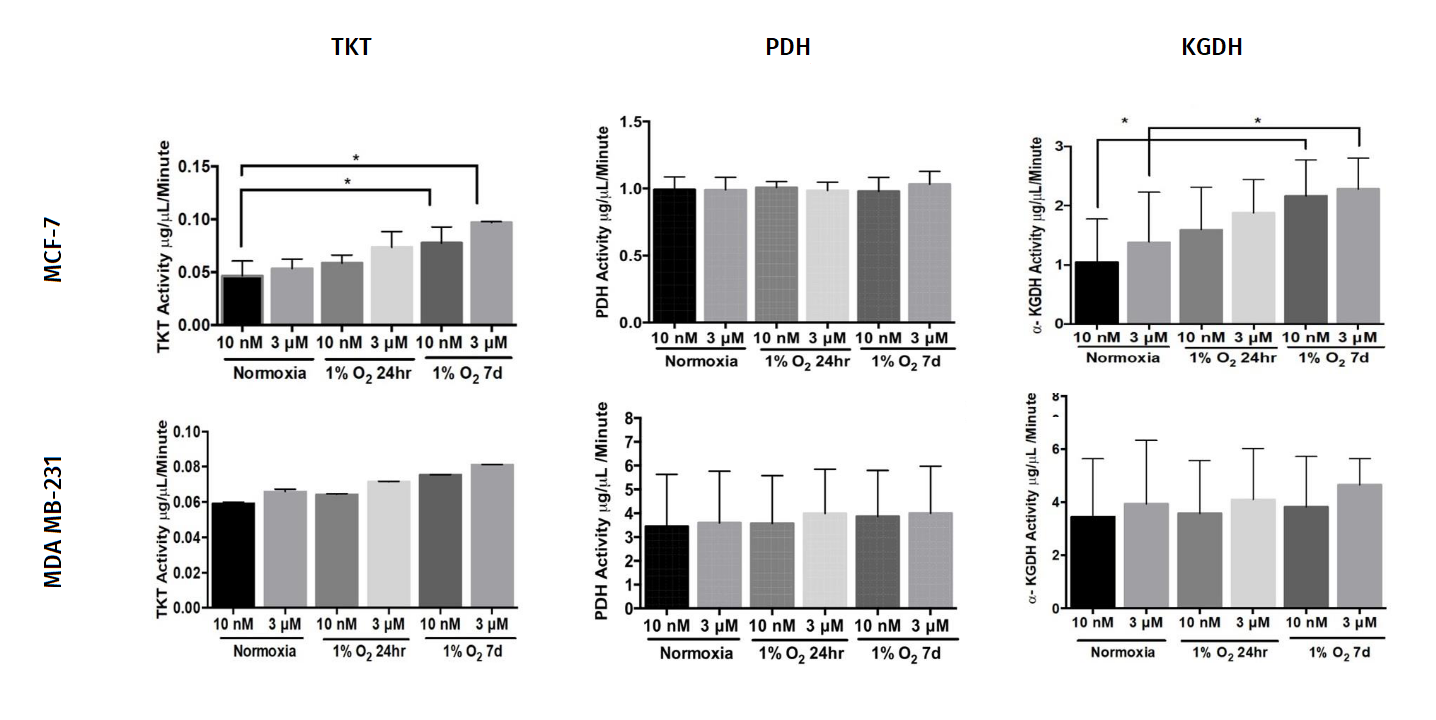
"The thiamine concentration in plasma is observed to be in the range of 10-20nM. We used 10nM thiamine concentration as a control group to simulate the physiological levels of thiamine observed in human plasma."
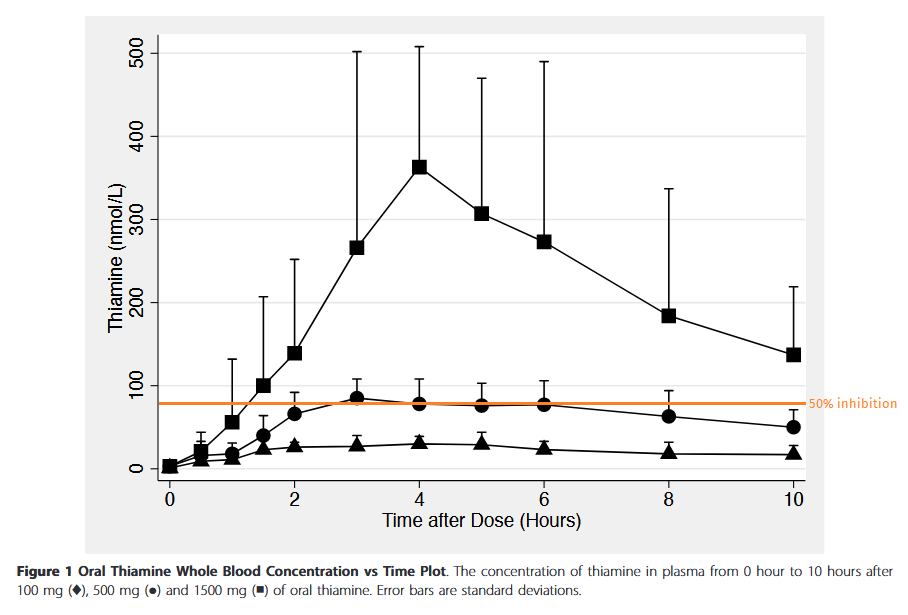
Below is a projection relying on maximum plasma concentrations after each oral dose (thiamin HCl).
Pharmacokinetics of high-dose oral thiamine hydrochloride in healthy subjects
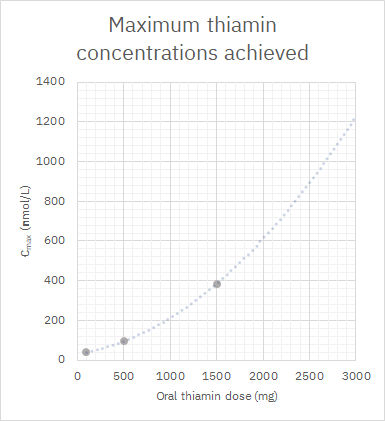
It's an optimistic curve. Suppose that rate keeps increasing and we reach a maximum concentration of 1200 nmol/L (0.0012 mmol/L or mM) with 3 g of oral thiamin (although the dose can get much higher without risk of toxicity). If you think that 3000 nM was an exaggerated level, the following experiment with cultured cells is often mentioned to defend supplementation:
High Dose Vitamin B1 Reduces Proliferation in Cancer Cell Lines Analogous to Dichloroacetate
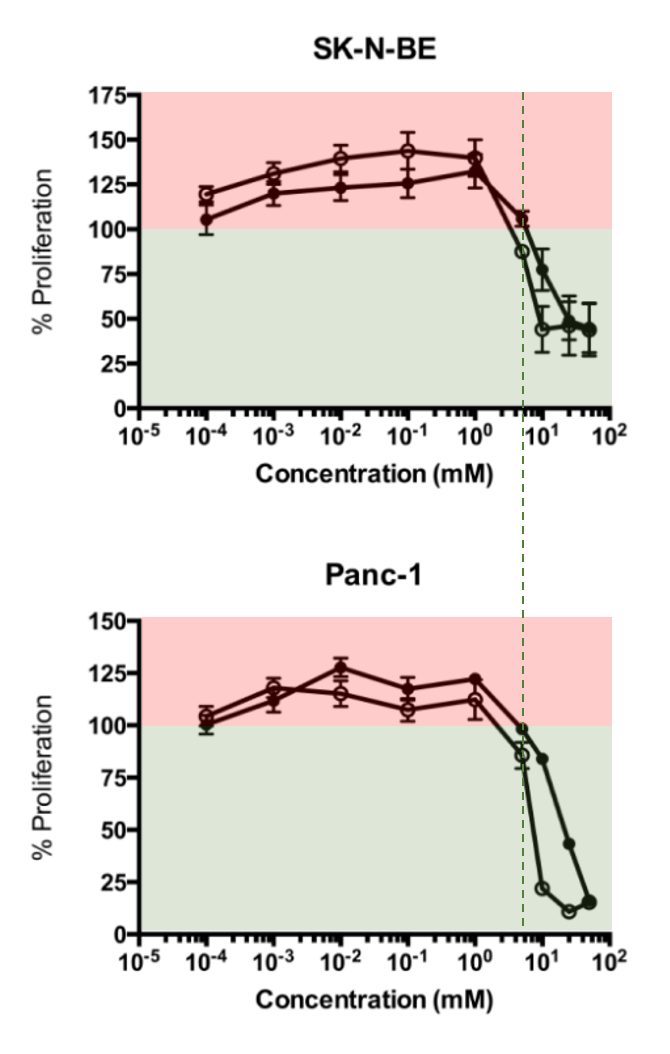
At about 2 mM (2,000,000 nM) of the tested concentrations is where they started to observe a decrease in proliferation. The half-inhibition concentrations were 4.9 and 5.4 mM.
Yet, we have this experiment that's more encouraging:
The effect of thiamine supplementation on tumour proliferation: a metabolic control analysis study
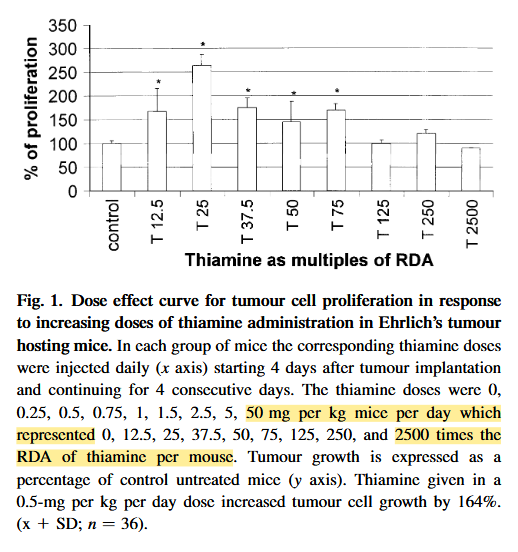
The highest dose led to a 10% reduction in proliferation. The extrapolated dose may be something like 250 mg/person, but administration was subcutaneous.
⠀(from here)In any case, for the overflow of thiamin to target PDH and make the effect prevail, the dose has to be extreme.
Considering the multiple influences on PDH, it remains possible that a major benefit of thiamin comes instead from its impact on carbonic anhydrases. Ray pointed out that it can work as an inhibitor and Jorge posted this experiment on the Antitoxin Forum:
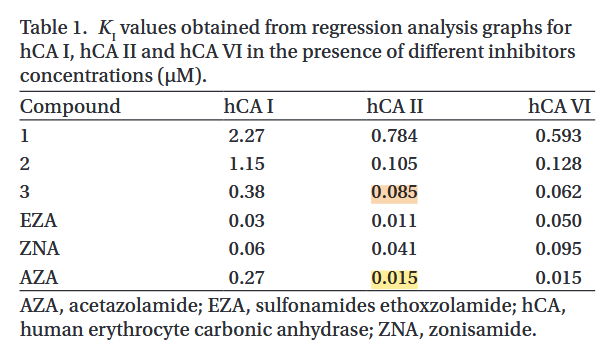
- Compound 3: thiamin
It's feasible:
Fingers crossed that it applies to other carbonic anhydrase forms as well.
The Expression of Carbonic Anhydrases II, IX and XII in Brain Tumors
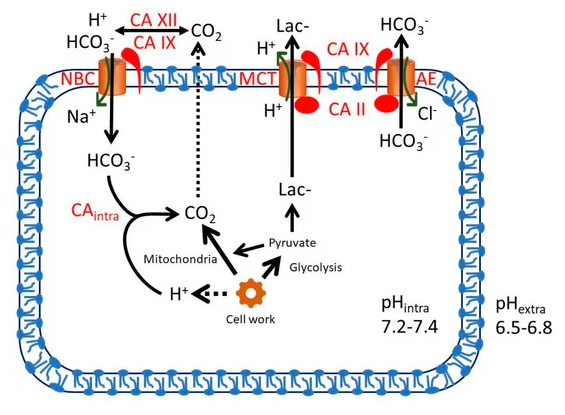
Despite carbonic anhydrases 9 and 12 being exposed on the surface of cells, the cells might be clustered in poorly vascularized tissues. If it's not a blood cancer, we can expect a sharp decrease in the thiamin concentration as we get to the core of this mass, which strengthens the idea that it's worth being extreme in supplementing it in cancer.
-
It's rarely mentioned that Ricky was also a thiamin pharmaco-enthusiast.
Warburg effect(s)—a biographical sketch of Otto Warburg and his impacts on tumor metabolism
"Warburg considered cancer to be a nutritional problem, one that could be avoided by maintaining an appropriate natural diet. As early as 1923, Warburg and Schoeller discussed starving cancer by drugs leading to “nutritional deprivation” [4]. In his last publication in 1970, he claimed that a cause for spontaneous “tumor metabolism” was either a lack of oxygen or a lack of vitamin B1 (thiamin)—both conditions increasing the production of lactic acid [25]. This line of thinking led him to consider the administration of vitamin supplements, which would enhance respiration and was considered to be a natural and safe application. Already in the 1940s, Warburg, who was asserted having cancer phobia, practiced his own recommendations in maintaining a disciplined lifestyle: he grew his own vegetables, drew water from an unpolluted well, had his bread baked with grains from wheat not treated with pesticides, and kept his own poultry. And, he did sports: long walks, horseback riding, or sailing [3]. After his favorite sister Lotte died of cancer in 1948, Warburg also quit smoking [4]. Warburg, being sensitized to the dangers of smoking, alcohol, and drugs, proposed to the German Ministry of Health to reduce cigarette smoking, motor vehicle exhausts, air pollution, and chemical additives in foods as cancer prevention measures. This was in 1954 and at that time without avail [3]."
↳ [25] Entstehung von Krebsstoffwechsel durch Vitamin-B1-Mangel (Thiaminmangel)
"Since the carcinogens known today produce about 80% of human cancer cases, one can prevent at least 80% of cancer by keeping carcinogens away from human cells. This leaves a remainder of at most 20% for "spontaneous" cancer, whose prevention is still a problem of science."
"We have developed a simple in-vitro test to investigate this problem. 10-day-old chicken embryos were divided into single cells using trypsin, which grew quickly in suitable culture media. Measuring the metabolism of such in vitro grown embryonic cells, one finds that either the purely aerobic metabolism, with which the embryonic cells grow in the body, is maintained; or that the embryonic metabolism switches to the fermentation metabolism of cancer cells. The switch can be reversible or irreversible. If it is irreversible, one can, based on all experiences of continued in-vitro cultivation, successfully transplant the fermenting cells onto animals."
"When applying the test, it has been shown that the switch from embryonic metabolism to cancer metabolism can be induced in two ways: either by temporarily placing B-vitamin-saturated cells under oxygen deficiency; or by temporarily placing oxygen-saturated cells under B-vitamin deficiency. Both methods have in common an inhibition of respiration, which must be irreversible and associated with an energy-equivalent increase in fermentation."
"Another result of the application of the test is that vitamin B1 occupies a special position among the B vitamins. Under our experimental conditions, the addition of 0.025 g per cm3 medium + vitamin B1, without the addition of other B vitamins, was sufficient to prevent the switch from embryonic metabolism to cancer metabolism, i.e., the development of cancer. Of course, this does not mean that the other B vitamins are unnecessary; but it only means that more vitamin B1 is required than the other B vitamins."
"The biochemical explanation is that the pathway of respiration and fermentation in the breakdown of carbohydrates to pyruvic acid is common, but then the pathways diverge, with pyruvic acid being hydrated to lactic acid by NADH on the fermentation pathway, while on the respiration pathway pyruvic acid is oxidized to acetic acid by vitamin B1. At the crossroads of respiration and fermentation, a competitive struggle between NADH and vitamin B1 for pyruvic acid takes place, in which respiration can only win if vitamin B1 is present in large excess over NADH."
"Medically, the consequence is that in the prevention of cancer by B vitamins, the dose of vitamin B1 should be increased as much as possible."
-
While Bulgaria is on a call with his supplier, sourcing the ingredients for Locketol, the polyphenol-based transketolase inhibitor, I would like to return to the previous experiment on thiamin functioning as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.
In such experiment, they used purified enzymes in direct exposure to a solution containing thiamin. We would have the tumor and the cell barrier. Concentrations of thiamin from massive doses probably decrease:
- Blood > Tumor with poor vascularization > Tumor cells
To achieve a free thiamin level of 85 nmol/L inside the cell must not be easy. And this half-inhibitory value is for the CA-2 (intracellular), not CA-9 and CA-12 (with superficial protrusions) that are more likely to encounter the high extracellular concentrations from exaggerated doses.
Proton Transport in Cancer Cells: The Role of Carbonic Anhydrases
"Measurements of CA-9 [CAIX] catalytic activity with gas-analysis mass spectrometry revealed that at a pH of 7.4, the enzyme's rate constant for hydration was faster than for dehydration [58]. At pH values below 6.8, however, the rate of dehydration exceeded the hydration rate. For pH 6.8, the rate constants for hydration and dehydration were essentially the same [58]. CA-9 displays an apparent pK of 6.84 and is inhibited at lower pH values [59]. Therefore, a low pHe could limit further H⁺-production by CA-9 in the extracellular space. In other words, at pH values below 6.8, CA-9 favors the dehydration reaction, while at pH values above 6.8 the hydration reaction is preferred [55]. Taken together, these observations indicate that CA-9 functions as a pH-stat that sets tumor pHe to an acidic value of around 6.8 [55–59]."
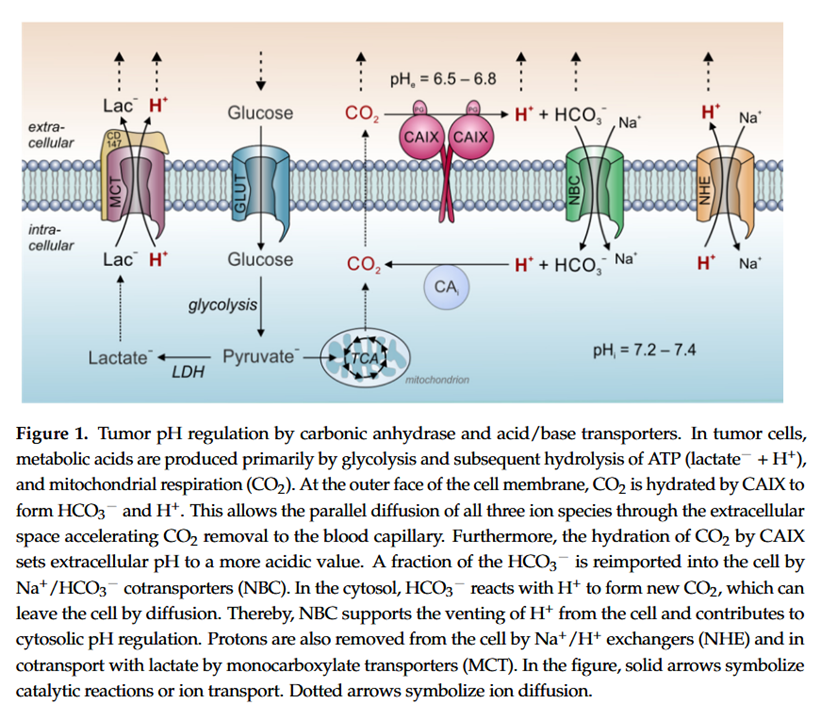
Therefore, if the inhibitory thiamin concentrations for CA-9 and CA-12 are similar to that for CA-2, a possible scenario is their inhibition without a simultaneous inhibition of CA-2 (one of the "CAi" shown above). In this situation, cells would continue to be alkalinized through the generation of CO2, but without its fast hydration on the other side.
The partial inhibition (on CA-9/12 without CA-2) would remain helpful. For example, in minimizing the degradation of extracellular matrix, easing the suppression of the immune system, and decreasing vascularization. Not being able to affect CA-2 wouldn't be too unfortunate because it's less specific to cancer, which would imply more burden to healthy cells along. Yet, if intracellular CAs are not targeted, the alkalinization inside the cell with CO2 formation would continue.
An advantage is that the lack of external hydration of CO2 may limit its diffusion, in special in a packed mass with poor circulation. The compartments would tend towards an equilibrium, and more CO2 inside the cell can compromise alkalinization.
The majority of thiamin occurs as thiamin diphosphate (TDP):
Perhaps not in blood after crazy doses, but possibly inside the cell. If TDP is another carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, its intracellular concentration can be high, with 949 nmol/L as an outlying example, and can add to the effect of free thiamin.
Also, compound 7 on the table below is salicylic acid:
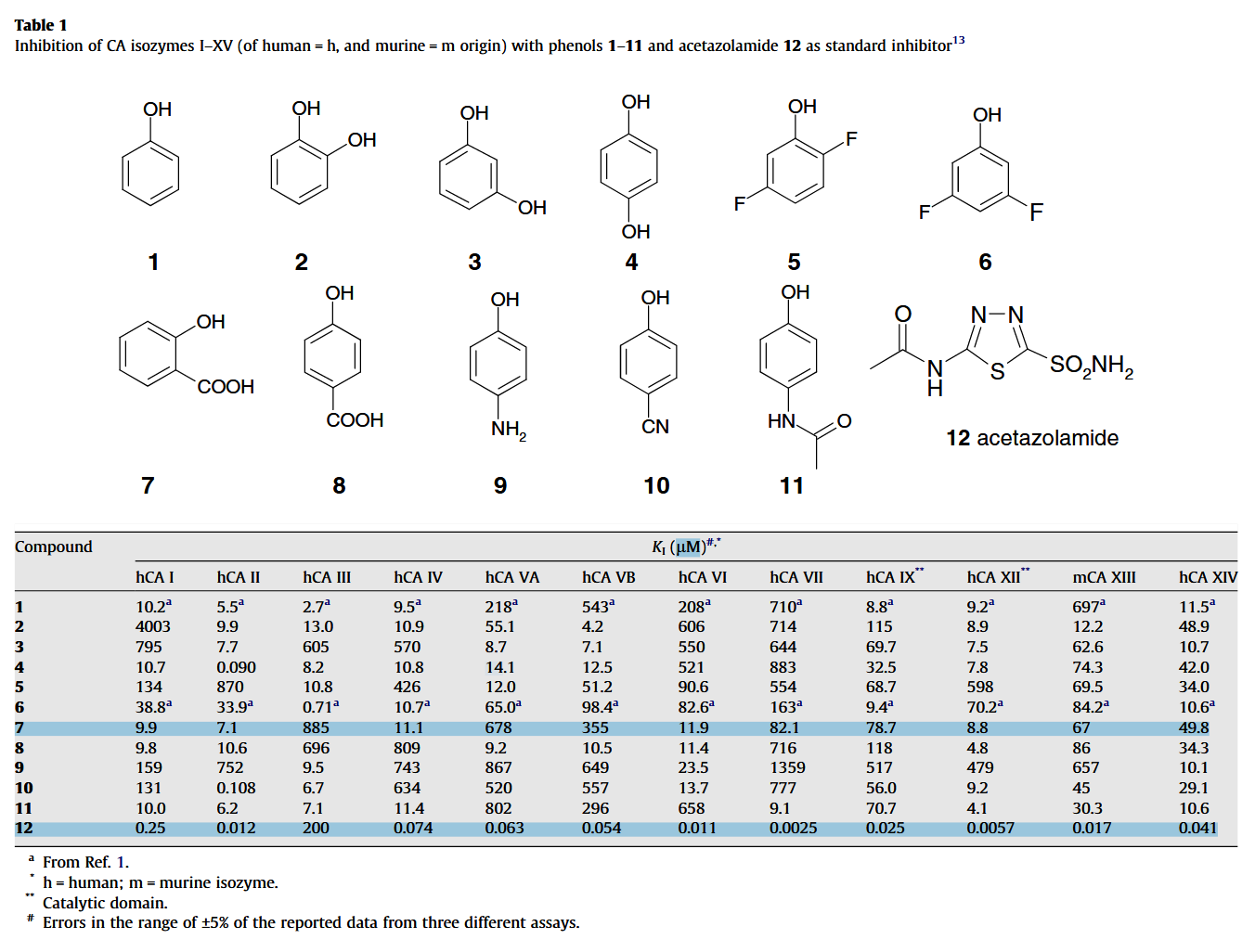
In a scenario where all target carbonic anhydrases are somehow inhibited and pyruvate is diverted from lactate, it would be good to verify if the alternative means to regulate proton concentration can't make up for it.
What is pH regulation, and why do cancer cells need it?
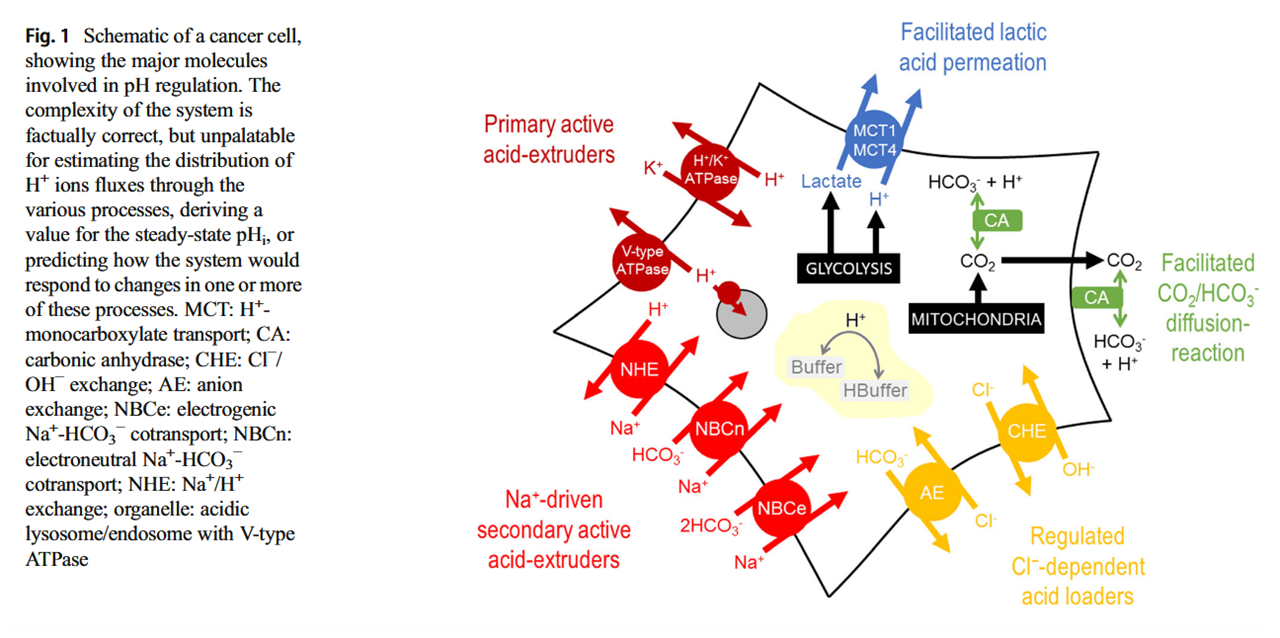
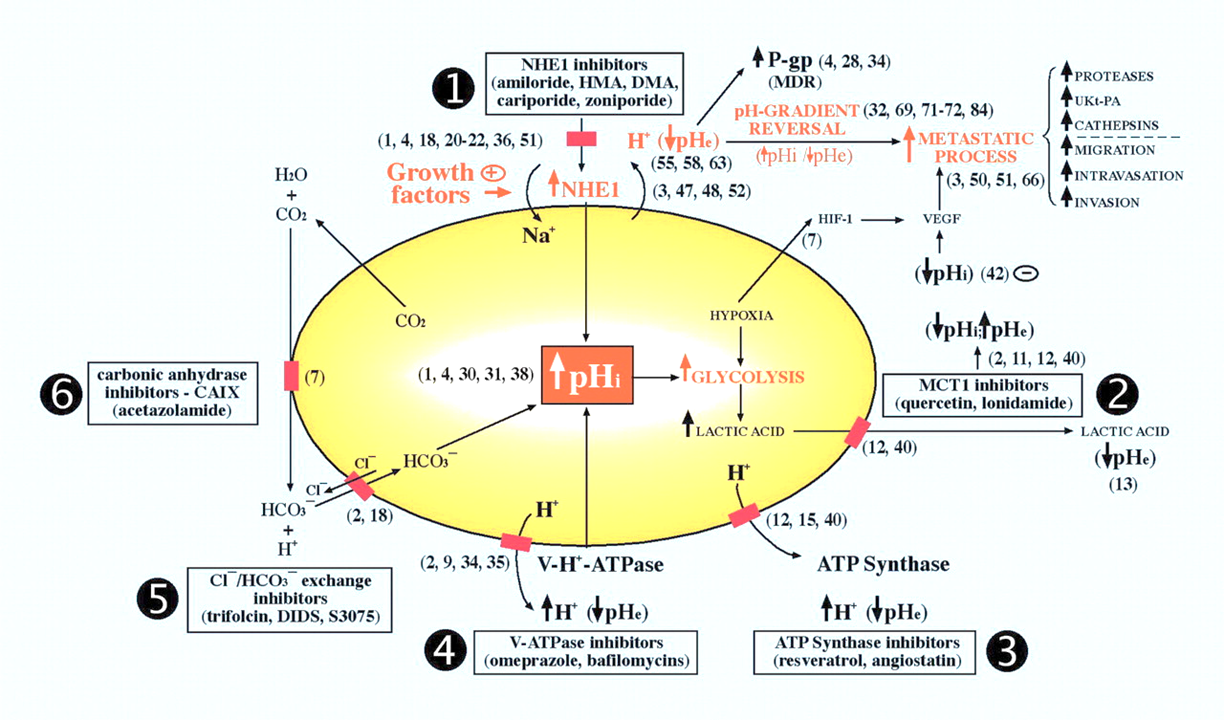
Manipulation of carbonic anhydrases impairs tumors and suggests that they're major contributors to the altered pH. But you can also find experiments where these other proteins were modified, resulting in compromised growth. They're druggable:
Proton Transport Inhibitors as Potentially Selective Anticancer Drugs
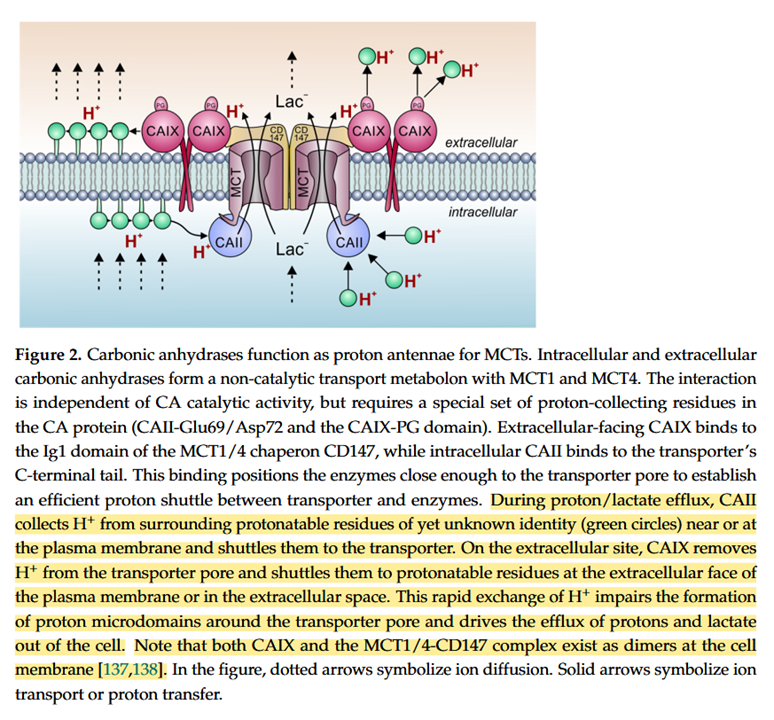
And inhibited carbonic anhydrases don't appear inert, they can occur near those proteins and may still cooperate with them in the transfer of buffered protons on either side:
Proton Transport in Cancer Cells: The Role of Carbonic Anhydrases
-
This is such fantastic work! I wish there was like a crowd funding system for this type of independent scientific research, I'd chip in money lol. And as a reward maybe give ppl the raw data and/or write up.
An interesting mix of B vitamins, why those 3 in particular? Anyone have the cliff notes?
Maybe those are good longevity health supps

-
@Amazoniac I wish I had the background to grasp all of what you wrote. From what I gathered, it looks like biotin may or may not be helpful, thiamine has some risks, but the benefits of saturating the body with enough to get in the cell most likely outweighs those risks in fighting cancer, as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (and aspirin is also a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.)
-
 L LucH referenced this topic on
L LucH referenced this topic on
-
Salicylate is a major plasma metabolite following high doses of aspirin. Perhaps about half of the dose occurs unbound in these cases. For an idea of reachable levels:
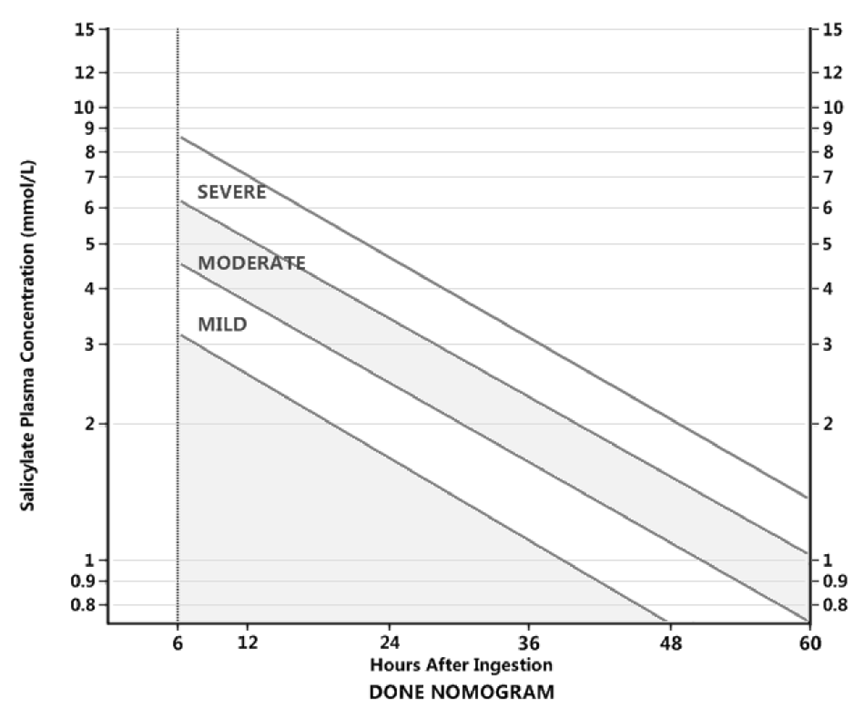
Up to 2.2 mmol/L is considered therapeutic.
The inhibition constant of salicylic acid for carbonic anhydrases was less than 0.1 mmol/L.
As a side note on aspirin as an inhibitor, the effect that it has on COX-1 is commonly treated only as an inconvenient in its use, but it may not be all problematic:
For carbonic anhydrases, acetazolamide outperforms the compounds in question in almost every CA tested, which is why it's used as reference. It's nice that the two experiments posted earlier (thiamin and salicylic acid on CA) arrived on similar values for acetazolamide.
To compare the responses:
-
Thiamin and niacin supplementation has more basis than biotin, but for each of them we can find potential concerns.
It's easier to explain the beneficial effects of these vitamins through their systemic effects. Nutrients are usually a mix of good and bad in cancer. Example:
- Potential Role of Magnesium in Cancer Initiation and Progression
- Magnesium and its transporters in cancer: a novel paradigm in tumour development
- Magnesium and neoplasia: From carcinogenesis to tumor growth and progression or treatment
- Magnesium and cancer: a dangerous liason
To anticipate the point on dual disinhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) from thiamin with niacin, I don't have clear if we have a dosing range where niacin (as niacinic acid or niacinamide) supplementation could be counterproductive.
The focus is on:
- ↑Niacin → ↑NAD⁺ → ↑PDC
But what about the cytosolic dehydrogenases?
Think of it: where can we expect additional NAD⁺ to be preferentially consumed, in a pathway that's intensely upregulated (glycolysis) or one that's downregulated (pyruvate oxidation)?
If additional NAD⁺ favors Glyceral-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GAPDH) in glycolysis, this could lead to the formation of more pyruvate, which then redistributes to new lactate, reinforcing the problem.
LDH is an efficient enzyme that prevails in excessive glucose catabolism. LDH regeneration of NAD⁺ is simpler and more assured than the elaborate mitochondrial shuttles and oxidative phosphorylation.
Saturation of the mitochondrial NADH shuttles drives aerobic glycolysis in proliferating cells
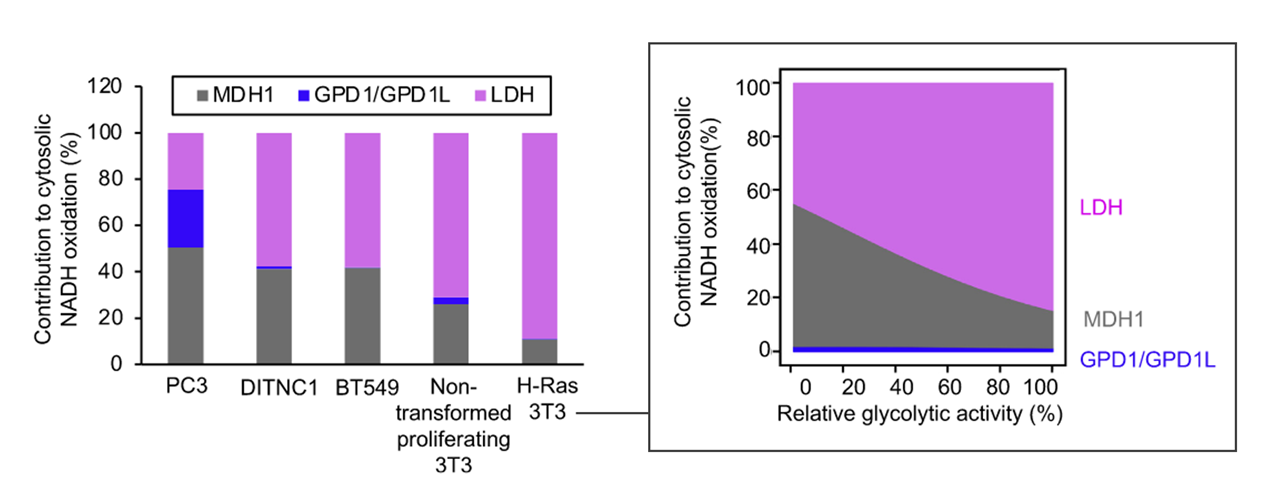
PDH has higher affinity for pyruvate than LDH, but lower capacity to metabolize it. PDH is also found in mitochondria, as opposed to the cytosolic LDH.
These sides are in equilibrium:
- Pyruvate + NADH + H⁺ ⇄ Lactate + NAD⁺
The form of lactate dehydrogenase expressed in cancer can be the A-dominant, with a set point in great bias towards lactate formation [→].
Where B-dominant LDH occurs, the site can be primed to recover pyruvate from lactate [←], and extra NAD⁺ could lead to an aggravation of the pattern.- Targeting lactate-fueled respiration selectively kills hypoxic tumor cells in mice
- Glucose feeds the TCA cycle via circulating lactate
Even though the concentration of metabolites can overcome the enzyme bias, in the presence of extra NAD⁺, A-dominant LDH should offer greater resistance to the recovery of pyruvate. This could result in a larger pool to maintain the following cycle running:
The Regulation and Function of Lactate Dehydrogenase A: Therapeutic Potential in Brain Tumor
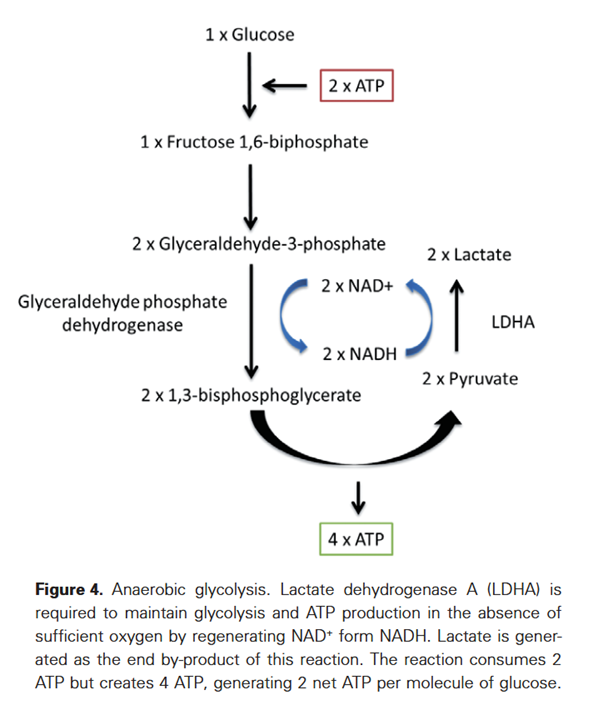
GAPDH doesn't seem to be a limiting step in upregulated glycolysis, but we can't discard the possibility that it may happen:
- Four Key Steps Control Glycolytic Flux in Mammalian Cells
- ↳ Quantitative determinants of aerobic glycolysis identify flux through the enzyme GAPDH as a limiting step
Local negative effects from additional NAD⁺ is not an unreasonable concern:
Increased demand for NAD+ relative to ATP drives aerobic glycolysis
PDH disinhibition decreased fermentation and proliferation rate as expected, but the decrease occurred along with lowering the NAD⁺/NADH ratio. Next, they found that it's possible to restore proliferation through artificial NAD⁺ regeneration. This regeneration of NAD⁺ defeated the first levels of PDH disinhibition, despite a reduction in fermentation.
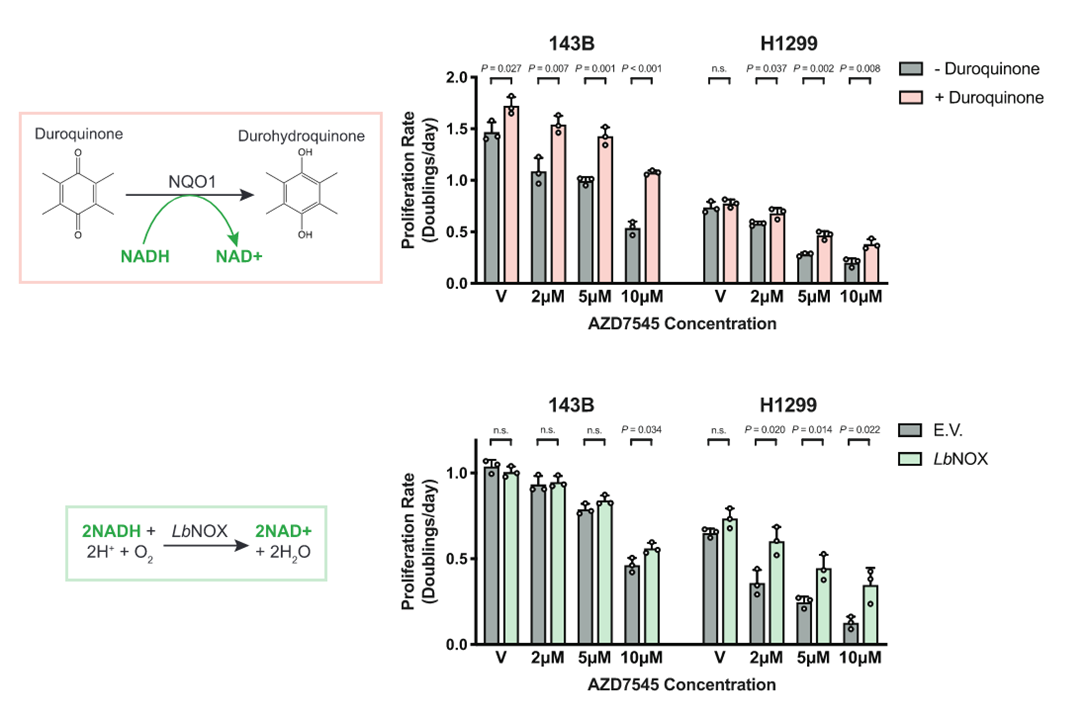
It also suggests that recycled NAD⁺ doesn't promote glycolysis, or at least not enough to counteract the share of pyruvate escaping fermentation.
The oxidation of NADH at Complex I is normally tied to ADP and Pi consumption (with proton dissipation) at Complex V. This dependency is a factor that limited proliferation. Additional NAD⁺ from supplements would be a way to bypass the protective limitation in the short term and it's an issue to consider.
We can also anticipate a comment on compartmentalization of NAD at this stage.
As before, we have the same mitochondrial dehydrogenase complexes (and others) competing for resources: PDC and KGDC. It's not difficult to imagine NAD⁺ favoring once again the uninhibited KGDC over PDC. In addition, if ketoglutarate (substrate of KGDC) is derived oxidatively from glutamate, why couldn't NAD⁺ promote its metabolism?
- Glutamate + NAD⁺ + H2O → Ketoglutarate + NH4⁺ + NADH + H⁺
Respiration can still occur when the availability of oxygen is low, but respiration is not the only way to reoxidize NADH formed inside mitochondria. The TCA cycle dehydrogenases working in reverse can serve this function:
- MDH: malate ↶ oxaloacetate
- SDH: succinate ↶ fumarate
KGDH cannot, just like CS (citrate synthase), the reaction is irreversible in humans as far as I know.- IDH: isocitrate ↶ ketoglutarate*
⠀*Part of the total ketoglutarate can be metabolized to succinyl-CoA and the other to isocitrate simultaneously.
Acute sources of mitochondrial NAD+ during respiratory chain dysfunction
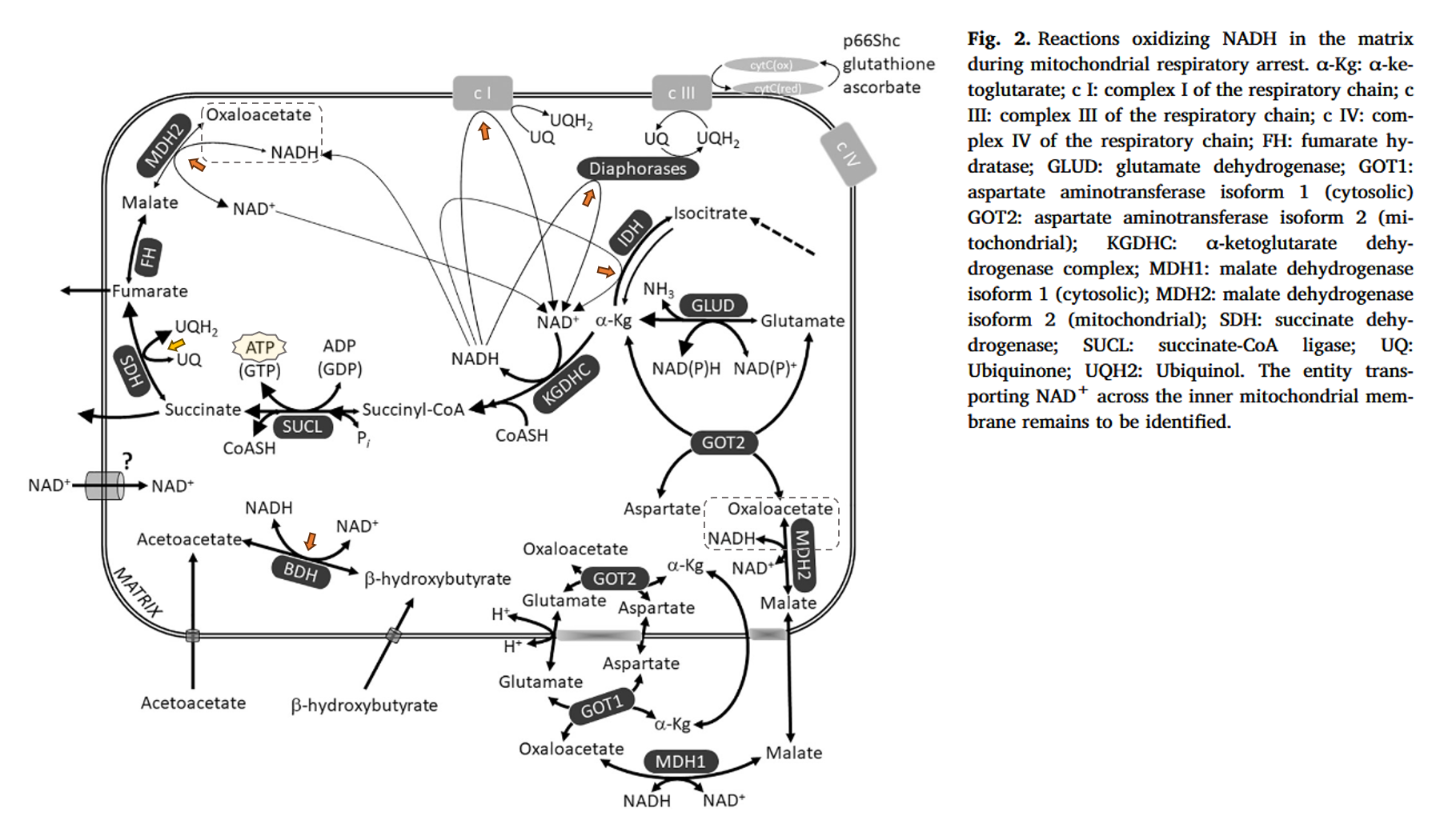
The reactions indicated are all regenerating NAD⁺ consumed by KGDC, without necessarily involving the electron transport chain (gray). Diaphorases would be the NAD(P)H:Quinone Oxidoreductases (NQO).
SDH (yellow) shown above should be included too:
- Fumarate is a terminal electron acceptor in the mammalian electron transport chain
- Residual Complex I activity and amphidirectional Complex II operation support glutamate catabolism through mtSLP in anoxia
The stressful reversal:
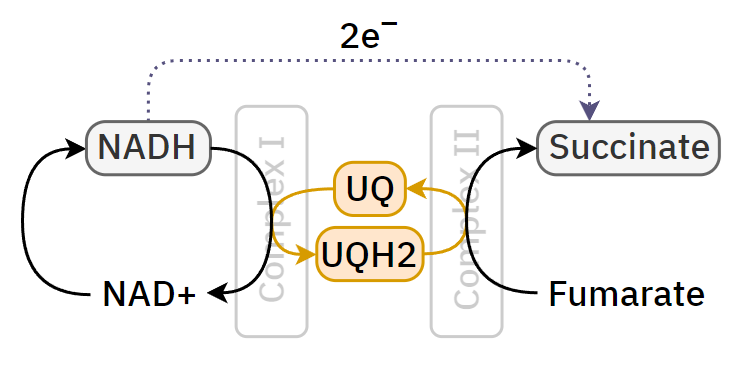
I'm bringing these up because NADH formed in mitochondria won't invariably force oxidative phosphorylation.
Mitochondrial substrate-level phosphorylation ('mSLP') that was mentioned occurs following ketoglutarate oxidation. It's a reaction that they emphasize as an overlooked source of ATP in cancer ('SUCL' on the previous figure).
On the Origin of ATP Synthesis in Cancer
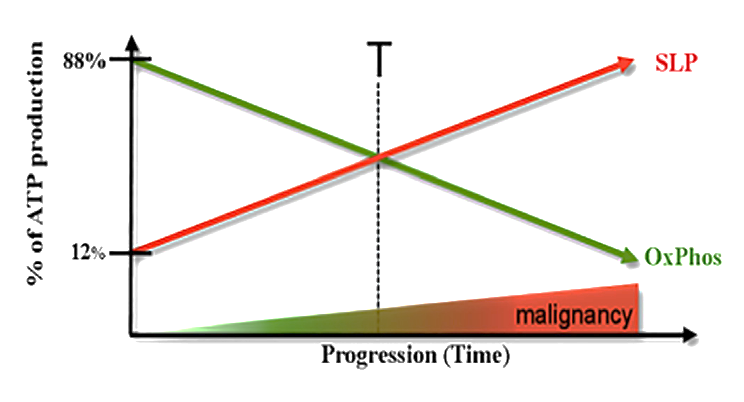
Process Yield/glucose cytosolic SLP 2 ATP (net) mitochondrial SLP 2 ATP (mitochondrial) OxP 28 ATP (varies) Total 32 ATP - (SLP ATP) ÷ Total ATP → (2 ATP + 2 ATP) ÷ 32 ATP ≈ 12% of energy from SLP in normal conditions
Some normal cells increase reliance on aerobic fermentation where the anabolic or antioxidant needs are high. How much fermentation and respiration occurs in cancer, where and when, is a long-standing debate. It's difficult to address a problem properly when we go by assumptions about its extent. Sidney Weinhouse began a series of valid questionings that are worth checking out:
-
We had a craze on the Ray Peat Forum where a few members started to take ascorbic acid reacted with methylene blue for being mesmerized by the change in color. Consider this:
- 5.68 mmol/1 g ascorbic acid
For a single reaction, this would call for 1.8 g of methylene blue per gram of ascorbic acid. People take methylene blue on the low mg range or even less, such as 150 mcg (0.00015 g). It's likely that they're downing the instant solution with only a small fraction of vitamin C oxidized. Note that the reason why they combine them is to consume preoxidized vitamin C.
And this is without taking into account the multiple cycles that ascorbate undergoes in the body, making external manipulations of low doses somewhat redundant. Also, that the pharmacological uses for a considerable oxidative burst are way off from their method:
Review of high-dose intravenous vitamin C as an anticancer agent
"Vitamin C has different functions at physiological and pharmacological plasma concentrations. Oral vitamin C administration is associated with tightly controlled plasma concentrations regulated by the pharmacokinetic principles of bioavailability and clearance.[7] Saturation of bioavailability mechanisms occurs at oral doses of 400 mg daily equating to blood levels of 60–100 μM.[8] IV dosing bypasses this tight control, achieving plasma concentrations up to 20 mM.[7,8]
In vitro evidence suggests plasma concentrations of 10 mM are necessary for an antitumor effect and this appears achievable clinically only with IV administration.[8] Padayatty et al. postulated that the vitamin C-free radical species, ascorbyl radical, forms only when human plasma concentrations are greater than 10 mM and that it is this radical or its unpaired electron that induces oxidative damage in cancer cells.[8]
Casciari et al. published a trial to determine the dose necessary to achieve this level in humans.[57] In a single patient with colon cancer, they found that a dose of 60 g but not 30 g was effective at attaining this. A recent phase I trial of 24 patients demonstrated that IV vitamin C to a dose level of 1.5 g/kg three times per week was safe and achieved plasma concentrations >10 mM for several hours.[58] While average follow-up was only 10 weeks, this trial did not demonstrate objective tumor response at these levels.[58] Riordan et al. published a series of 24 patients treated with IV vitamin C 150 mg/ kg/day and 710 mg/kg/day.[59] The mean plasma level was 1.1 mM (below the expected therapeutic target). They did not demonstrate a correlation between dose and plasma concentration. The reason for this is unclear. Other factors such as critical illness, renal function and chemotherapy regimens may alter plasma vitamin C concentrations and affect the plasma concentration necessary for cytotoxicity.[58]"
You can find different values depending on the source, incomplete stalling, and ways to lower the effective dose, but the point is that to stand a chance to induce oxidative stress in distant cancer cells, the acute amount is much higher.
Ray was concerned about contaminants in synthetic ascorbic acid and would possibly sweat at the idea of combining it with an oxidant. Member 'jyb' alerted that methylene blue products can also be contaminated. It seems better to take them separately and renew the vitamin C dose often when you can't brutalize.
Related to the previous topic, Max Gerson and Ray endorsed niacin supplementation, but in moderate and repeated doses. Max recommended niacin (50 mg*) along with vitamin C (500 mg*) and aspirin (325 mg*), to be used orally multiple times a day. *If I'm not wrong.
-
@haidut @Amazoniac @Mauritio Here's something unexpected in breast tumors,
EDIT: its in HER2-enriched breast cancer , so showing nuance between cancers here
using acetazolamide (most potent carbonic anhydrase inhibitor) surprisingly they said it caused tumors to grow. even though tumor pH lowered, and lactate lowered
https://breast-cancer-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13058-023-01644-1#Sec16
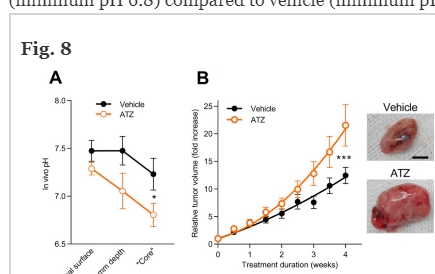
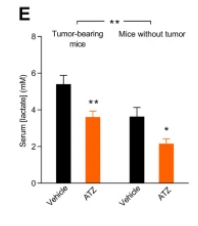
so the beneficial Apoptosis effect you'd usually see happen in hypoxic cancered cells from the lower pH is hindered / prevented by another effect?
It didnt raise proliferation markers, didnt raise vessel growth,The density of macrophages is high, T cells moderate, and B cells low; yet overall the abundance of these cell types is reduced by around half in breast cancer tissue from mice treated with acetazolamide compared to vehicle
so by the looks of it the lowered immune cell infiltration prevented the pro apoptosis effect
the extracellular carbonic anhydrases positively predict patient survival in HER2/ErbB2-enriched breast cancer
These observations suggest that carbonic anhydrases—likely via their ability to elevate tumor pHo (Figs. 6 and 8A)—provide an immune-stimulatory input that improves survival of patients with HER2-enriched breast cancer characterized by a weak immune response.
In contrast to HER2-enriched breast cancer, the association between extracellular carbonic anhydrase expression and patient survival in Basal-like breast cancer is seemingly unaffected by tumor inflammation
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/oncology/articles/10.3389/fonc.2023.1268421/full Acidification of intracellular pH in MM tumor cells overcomes resistance to hypoxia-mediated apoptosis in vitro and in vivo
Hypoxia-mediated apoptosis of MM cells is correlated with acidic intracellular pHi (less than < 6.6) that is dependent on HIF activity. a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (acetazolamide), and an NHE-1 inhibitor (amiloride) acidified the pHi and lead to cell death.
In contrast, treatment of cells with an alkalization agent, Na-lactate, rescued these cells by increasing the pHi (pH > 6.6). Finally, treatment of mice with acetazolamide decreased cell growth in the tumor nodules.{{interestingly just 40 MICROgrams/kg i.p was used to slow tumor growth there)
So this approach should be effective in cancers not characterised by weak immune response , but for those that are, its detrimental to lower pH , (at least without added ph independent immune stimulus overcoming its inhibition , if possible)
(or maybe need to really drive the pH down lower to hit <6.6 ,
so no half measures there? but i think the 1st study already would have hit most of the CA IX inhibition/co2 raise with 40mg/kg i.p right?here 40mg/kg orally inhibited lung tumor growth a little , and drastically lowered metastasis. so whether its a helpful or harmful effect does seem dependant on immune cell characteristics (otherwise if it worked at this dose here, it shouldnt have raised growth in the other) http://www.chinaphar.com/article/view/7735/8235
-
I came across a claim that cancer hypoxia can be explained by the lack of sufficient carbon dioxide production, invoking the Bohr effect for this.
- Carbon dioxide helps in oxygen offloading from hemoglobin, but it's not an imperative factor. It would have been more appropriate to argue in terms of uncontrolled and fast growth outpacing the ability to properly vascularize the mass, leading to poor oxygenation.
- Cancer cells can produce substantial amounts of carbon dioxide with the aid of cytosolic carbonic anhydrases.
- Suppose that the external carbonic anhydrases (↓CO₂) overwhelm the internal ones (↑CO₂), to the point of depleting carbon dioxide. However, the effect of carbon dioxide on hemoglobin is primarily mediated by acidity from carbonic acid deprotonation.* Tumors will form plenty of carbonic acid and tend to have the surroundings extraordinarily acidic, so it remains possible that this acidity reaches hemoglobin, which circulates in blood rich in hydrocarbonate ions.
- Carbon dioxide is just one of the factors affecting the oxygen-hemoglobin association. Not surprisingly, acidity, temperature, and glycerate-2,3-bisphosphate also influence its behavior. In tumor thermography, they take advantage of overactive cancerous tissues being warmer than healthy ones.
The oxygen affinity of Hb is influenced by H+ in a manner termed the Bohr effect. In capillaries of metabolizing tissues, CO2 enters RBCs where it is rapidly converted to H2CO3 by carbonic anhydrase (carbonate dehydratase). This carbonic acid spontaneously ionizes to H+ and HCO3−. The increased H+ concentration decreases the oxygen affinity of Hb and facilitates oxygen delivery to the tissues.
The direct binding of CO2 to Hb in carbamino groups also lowers oxygen affinity, but this effect is considered to be minor.