Oxygenated,
You're making one categorical affirmation after another with a conviction that contrasts with the attitude of authors in this field, who are conservative for being aware of the volume of unreliable or contradictory information on the topic.
Already in the title, you declared that fat oxidation is the main source of cellular ROS, but how did you conclude this?
[image: 1754347668994-029bee82-cd38-4ff1-aeb7-28846684e250-image.png]
⠀(10.1242/jeb.221606)
In pink are the major sources:
[image: 1754347697643-dac6e475-a2b8-42a9-babc-92ed6b2fc234-image.png]
⠀(10.1038/s41580-020-0230-3)
[image: 1754347722481-da7b76ab-128b-4dfb-8524-02fee5516ac3-image.png]
⠀(10.1038/s41580-020-0230-3)
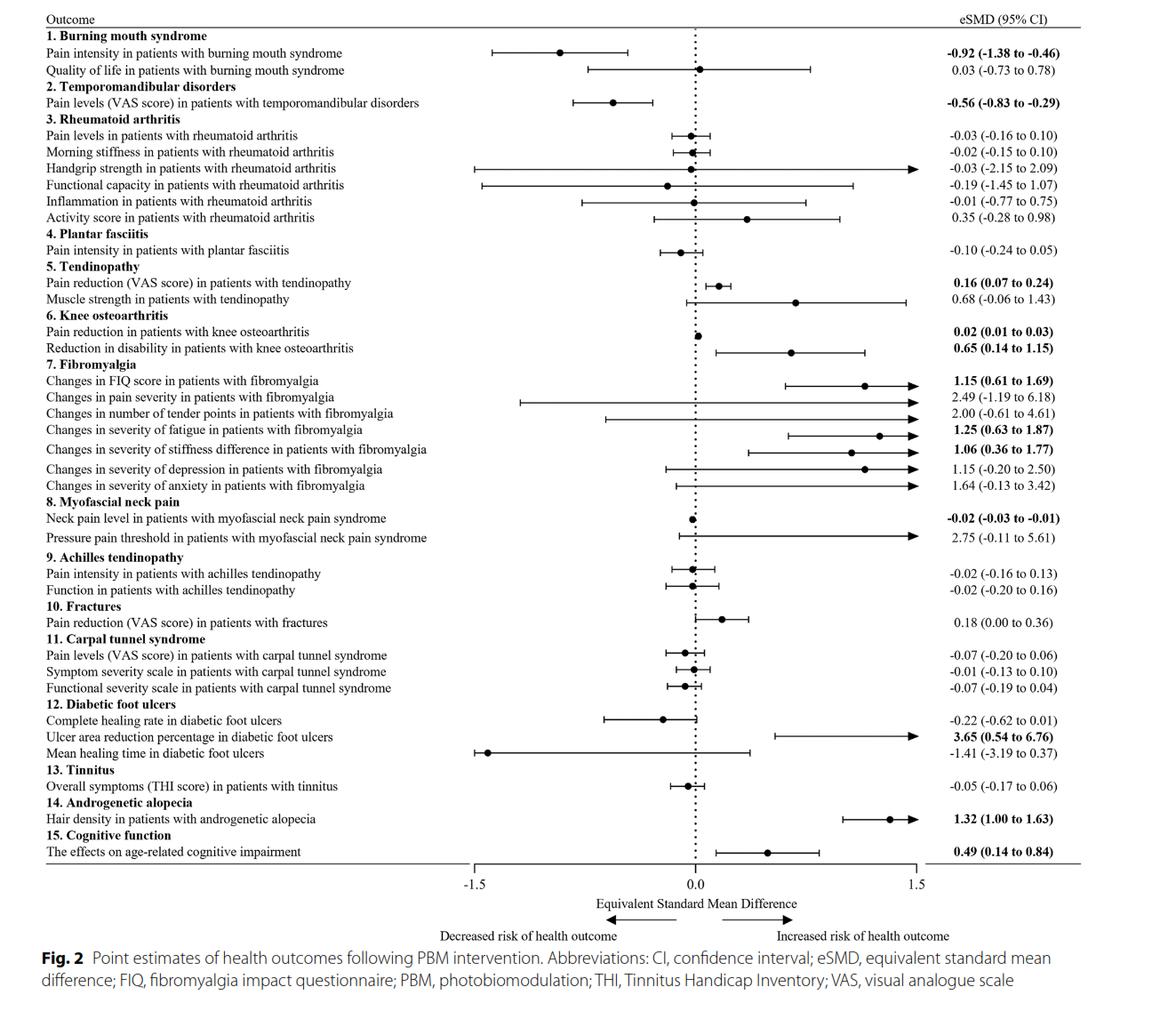
It would be worth clarifying how each of these H₂O₂ is generated, as we could have yet another statement put to question: that ROS formation involves unpaired electrons. Example:
"[..]complex I could mediate one- or two-electron reduction of oxygen[..]" (10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.01.002)
[image: 1754347771554-786c9b7d-f263-4d02-ad31-1196acfc643a-image.png]
⠀(10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141701)
We know that oxidases generate H₂O₂, which already challenges the exclusive association of ROS with one-electron reactions.
Nevertheless, even if we relax the criteria to include other ROS sources related to fatty acids (peroxidation and eicosanoid metabolism as examples), we would still be left with comparable alternatives to consider, such as NADPH oxidases (NOX).
[image: 1754347859260-7c318a3d-f274-44da-9199-9fa83e96b037-image.png]
⠀(10.1016/j.redox.2020.101722)
[image: 1754347869418-2f9790b8-96fe-438d-81f6-21dbb7593dd7-image.png]
⠀(10.1242/jeb.221606)
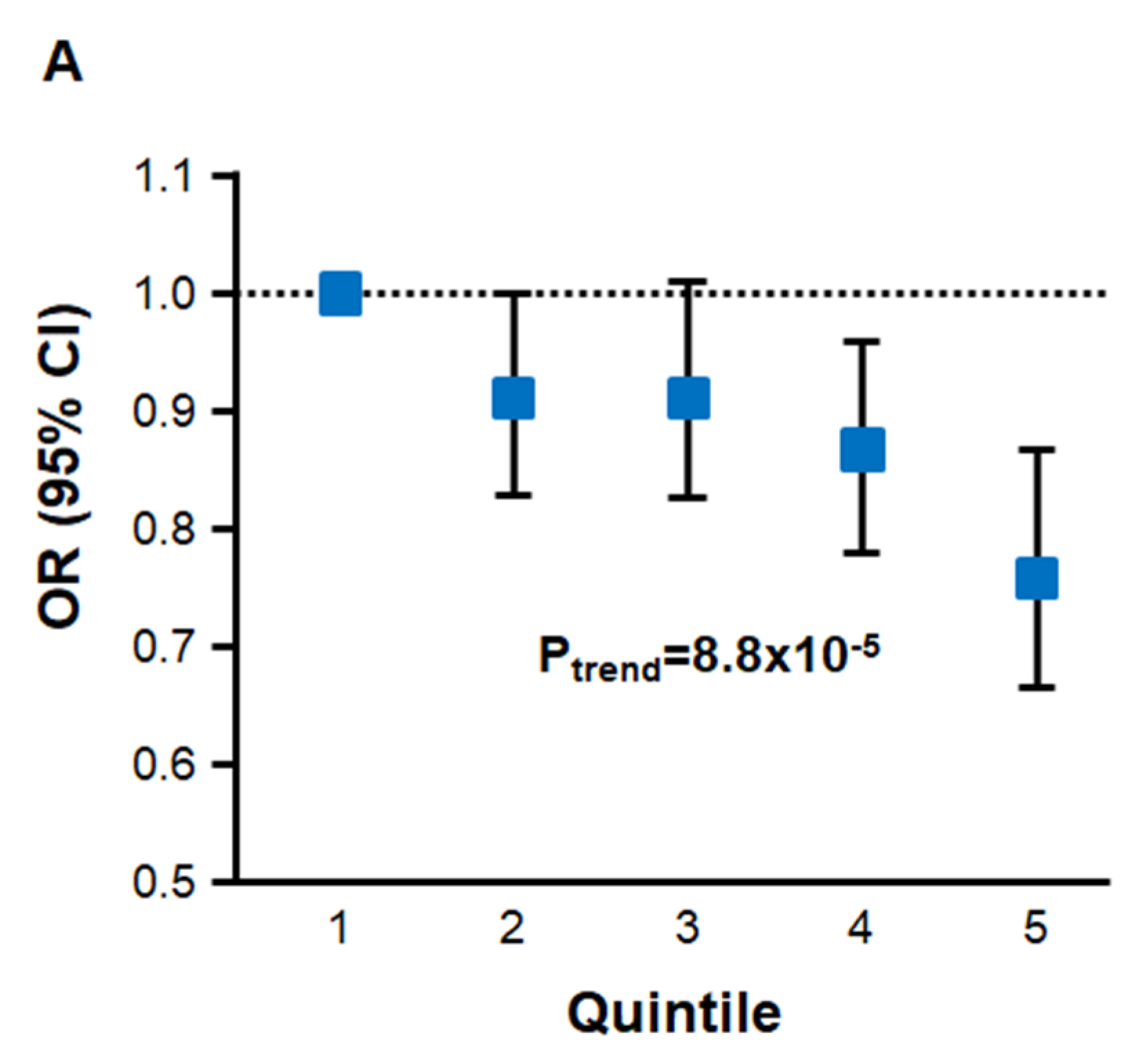
You can tell that a fraction is attributed to mitochondria. Then, only part of this mitochondrial (and peroxisomal) ROS will come from fatty acid oxidation in normal conditions.
Cellular ROS > Mitochondrial ROS > Fatty acid oxidation ROS
With conclusive information about the contribution of each compartment, we would have to discount all ROS sources unrelated to the oxidation of fatty acids, our latest carcinogens on the block.
Funnily, with glucose oxidation, every opportunity to maximize ROS production is taken as a room for cancer therapy. With fatty acids, when the opportunity appears, the picture is carcinogenic and let's leave the interpretation at that, without conceiving exploiting this "massive" burst of ROS to potentiate eradication therapies.
Different from many doctors, most researchers in the field are well-aware of the association of stimulated oxidative phosphorylation with lower ROS production, an observation that has been circulating since early publications:
"Addition of succinate speeds up H₂O₂ production by a factor of six and, after that, the addition of ADP (state 4 → state 3 transition) (Chance & Williams, 1956) decreases it to a value similar to that in the absence of substrate. When all the added ADP is phosphorylated, there is an acceleration paralleling the changes in the mitochondrial metabolic state. A further addition of ADP produces the transition to the active state, with the corresponding slow rate of H₂O₂ production." (10.1042/bj1280617)
But a higher metabolic rate doesn't inherently lower ROS production. It's a matter of electron availability around susceptible sites. Oxygen consumption is usually tied to ATP production, and increasing the need for ATP tends to increase the rate of respiration. Then, with a higher metabolic rate, the demand for electrons tends to decrease their availability, clearing the way for an orderly electron movement while reducing the chances of leakage. Likewise, a low metabolic rate with accompanying low rate of substrates oxidation must be able to get respiratory ROS production under control.
⠀
"Not only does reverse flow result in a dramatic shift of the redox status towards reduction, but the build-up of ROS leads to direct structural damage to various cell proteins, as well as any intracellular structure containing polyunsaturated lipids."
More like the other way around: an abnormal change of the redox status in favor of reduction results in reverse electron flow. Electron accumulation precedes the redistribution.
⠀
"What has not been widely acknowledged is that in the absence of exogenous agents capable of blocking or more of the ETC complexes (e.g rotenone, metformin, etc), reverse electron flow happens quite easily and is in fact responsible for the majority of ROS production simply as a result of shifting the metabolic substrate from glucose to fat (Randle Cycle). Namely, if the Randle Cycle (RC) shifts sufficiently in favor of fat oxidation, that results in depletion of the FAD co-factor, and thus a block at ETC Complex II. In other words, all that is needed for massive generation of ROS is to switch from oxidizing primarily glucose to oxidizing primarily fat. That sounds shocking and counter-intuitive, considering the world (and medicine) has gone crazy over low-carb diets lately, but it is well-known and undisputed biochemical fact."
Putting aside the authoritative "undisputed biochemical fact", you have constructed the argument concerned with ROS overproduction from acute substrate alternation ("to switch"), only to then abruptly invoke chronic fatty acid oxidation ("low-carb diets"). These are different scenarios that can't be lumped together.
Why the need for alarmism? The term "massive" might be more suitable for describing Kvothe's reproductive organ (..I've heard) or the overwhelming ROS production that often occurs when blood flow is restored after a period of interruption, leading to severe tissue damage. However, reverse electron flow can also occur in a controlled, transient fashion, serving to induce beneficial adaptations.
It's odd that you reduced the problem to SDH 'blockage' from FAD depletion. If this was the case, why would it trouble cells that are primed to metabolize fatty acids as an adaptation to frequent exposure? Once the body synthesizes enough flavins to meet predictable needs (including everyday perturbations), it's a matter of maintenance to replenish obligatory losses from flavoproteins, and these are modest in relation to their extensive recycling in reactions. Fatty acid metabolism has to remain dependable in stressful conditions, and these are associated with micronutrient shortage.
Also, how do you explain the ability of mitochondria to oxidize copious amounts of plain succinate when incubated with it? Not only in isolation, but especially in the presence of other substrates that help to clear inhibitory oxaloacetate. If other substrates can enhance the oxidation capacity, it becomes questionable to argue in terms of flavins repurposing.
For succinate to become a SDH inhibitor itself, levels have to get extremely high while possibly involving an inability to wash it out, as when local blood circulation stops. Nevertheless, FAD should remain intact in SDH, which is why succinate can be readily oxidized when oxygen levels are restored in the tissue. In some situations, the purported SDH blockage could actually be protective, such as when SDH is intentionally inhibited by malonate to prevent ROS overproduction in classical reverse electron flow.
Complex I ← UQ ← SDH ← Succinate
Complex I ← UQ ← SDH ↚ Succinate
If you had in mind reverse electron flow in the broad sense, the immediate concern in the respiratory chain for upstream processes would be impaired Complex I activity due to competition for available ubiquinone. Complex I is responsible for reoxidizing NAD for matrix dehydrogenases dependent on it, that in turn are overlooked sources of ROS.
Altogether, it's a peculiar approach. What to make of it?